What is a Geomembrane?
A geomembrane is a continuous, impervious layer made from synthetic materials such as High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE), Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE), Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC), and others. These membranes are used as liners or barriers to prevent the leakage of liquids or gases in various industrial and environmental applications. They are particularly valued for their strength, durability, and water-resisting properties.
Types of Geomembranes
1. High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) Geomembranes:
•Description: Made from high-density polyethylene, HDPE geomembranes are known for their exceptional chemical resistance, UV stability, and tensile strength.
•Specifications: Thickness ranges from 0.5 mm to 3.0 mm.
•Advantages: High tensile strength, chemical resistance, UV stability.
•Disadvantages: Can be brittle at low temperatures, susceptible to punctures.
•Applications: Landfills, wastewater containment, pond liners, and secondary containment systems.
2. Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE) Geomembranes:
•Description: Made from low-density polyethylene, LDPE geomembranes are more flexible and easier to install than HDPE.
•Specifications: Thickness ranges from 0.5 mm to 3.0 mm.
•Advantages: Flexibility, ease of installation.
•Disadvantages: Lower tensile strength, less chemical resistance.
•Applications: Temporary containment, agricultural ponds, and linings for small-scale projects.
3. Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) Geomembranes:
•Description: PVC geomembranes are flexible and can be welded easily. They are often used in applications requiring flexibility and ease of installation.
•Specifications: Thickness ranges from 0.5 mm to 2.0 mm.
•Advantages: Flexibility, easy welding, good chemical resistance.
•Disadvantages: Can degrade over time, especially in UV exposure.
•Applications: Water reservoirs, fish ponds, and temporary containment systems.
4. Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) Geomembranes:
•Description: EPDM geomembranes are highly durable and resistant to a wide range of chemicals and environmental conditions.
•Specifications: Thickness ranges from 1.0 mm to 2.0 mm.
•Advantages: Excellent UV and weather resistance, long lifespan.
•Disadvantages: Higher cost, less tensile strength compared to HDPE.
•Applications: Roof membranes, water storage tanks, and swimming pools.
5. Bentonite Geomembranes:
•Description: Bentonite geomembranes are composite materials that combine a layer of bentonite with a geosynthetic material. They are self-sealing and highly impermeable.
•Specifications: Thickness ranges from 2.0 mm to 5.0 mm.
Production Process of Geomembranes
1) Film blowing process
ü The blown film process requires the film bubble to be inflated, and has certain requirements for the strength of the resin melt. If the melt strength is too low, the film will fall. The flat extrusion process does not have a film bubble inflation process, and the requirements for the resin melt strength and resin quality are reduced.
üCompared with the flat extrusion process, the membrane bubbles can be blown and stretched effectively, and the mechanical strength of the geomembrane prepared with the same resin can be improved.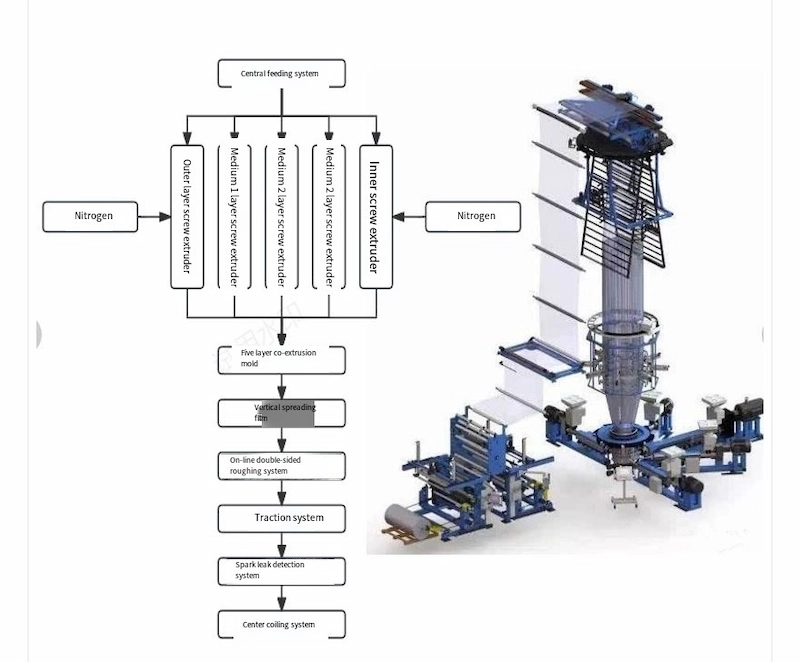
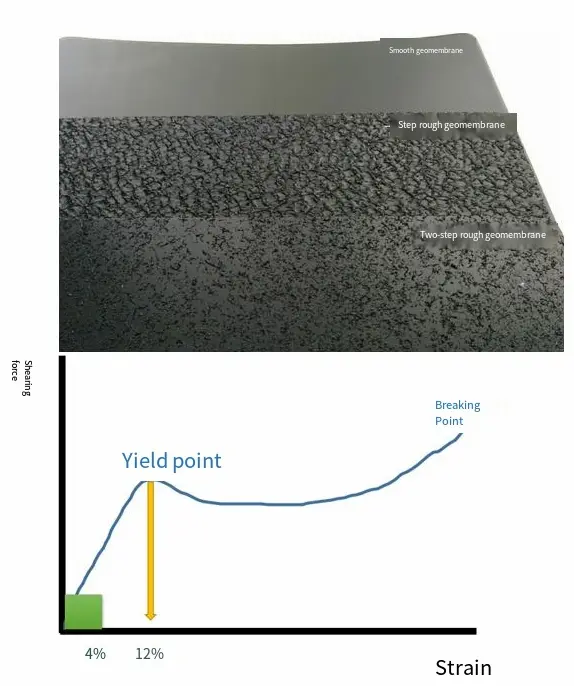
2) Co-extrusion process and roughening process
ü Co-extrusion process: During the preparation of geomembranes, the surface layer of the membrane is co-extruded with the gas source in the molten state to form a rough surface layer.
The advantage is that the rough surface layer is uniform and not easy to separate from the middle layer.
ü Roughening spraying process: The molten HDPE polymer is sprayed on the smooth geomembrane that has been prepared.
The advantage is that the mechanical properties are less damaged and the elongation at break is high.
In actual engineering, yield is often used as a sign of material failure. For rough geomembranes, the performance of products prepared by co-extrusion and roughening spraying is the same when yielding, and they have the same safety factor for engineering.
Specifications of Geomembranes
Material | HDPE, LDPE, PVC, EVA, etc. |
Thickness | Ranges from 0.5 mm to 3 mm or more, depending on the application. |
Roll size | Geomembranes are typically available in rolls ranging from 4 meters to 8 meters in width, with lengths of up to 100 meters or more. |
Weight | The weight of a geomembrane varies depending on its thickness and material. It is generally between 1 to 3 kilograms per square meter. |
Color | Most geomembranes are black (for UV protection), but they can also be green, blue, or white, depending on the application. |
Tensile Strength | The ability of the membrane to withstand pulling forces without breaking. This is crucial for applications that experience mechanical stress |
Elongation | Refers to the membrane's ability to stretch without tearing, important for accommodating ground movement. |
UV Resistance | Some membranes are treated with additives to improve their resistance to ultraviolet (UV) rays. |
Chemical Resistance | Some membranes are treated with additives to improve their resistance to ultraviolet (UV) rays. |
Pros&Cons of Geomembranes
Pros of Geomembranes:
1.Excellent Waterproofing and Sealing: geomembranes are highly impermeable, making them effective for preventing the leakage of liquids, such as water or chemicals, in landfill liners, reservoirs, and ponds.
2.Durability: they are resistant to various environmental factors, including UV radiation, temperature fluctuations, and chemical exposure, making them durable and long-lasting.
3.Cost-Effective: while initial installation may seem costly, geomembranes can be more affordable in the long run due to their low maintenance costs and extended service life.
4.Easy Installation: geomembranes are relatively lightweight, flexible, and can be easily cut and welded, making them easier to install compared to other traditional methods.
5.Versatility: these membranes can be used in a wide range of applications, including landfills, reservoirs, mining, water containment, and civil engineering projects.
6.Environmental Protection: they help to prevent soil contamination by limiting the infiltration of hazardous substances or leachate from landfills and other waste containment systems.
7.High Strength: they have excellent tensile strength, which provides the necessary support to withstand external pressure, such as soil and water loads.
Cons of Geomembranes:
1.Vulnerability to Mechanical Damage: while geomembranes are strong, they can still be punctured or damaged by sharp objects, construction equipment, or improper installation, which could lead to leaks.
2.Sensitivity to UV Degradation: prolonged exposure to direct sunlight can degrade the material over time, though this can be mitigated with UV-resistant additives or protective covers.
3.Temperature Sensitivity: some geomembranes may become brittle at very low temperatures or soften at high temperatures, which can affect their performance in extreme climates.
4.Environmental Impact of Production: the manufacturing of certain geomembranes (especially PVC-based ones) may have an environmental footprint due to the chemicals used and energy consumed during production.
5.Expensive Initial Cost: the upfront cost of geomembranes, especially high-quality materials like HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene), can be relatively high compared to traditional materials.
6.Limited Flexibility in Certain Applications: in some instances, geomembranes may lack the required flexibility to conform to complex or irregular subgrades, making them less suitable for certain applications without additional measures.
7.Difficulty in Repairing Damage: if a geomembrane is damaged, repairing it can be challenging and costly, requiring specialized equipment and materials to ensure the integrity of the seal.
Applications of Geosynthetic Membranes
Geosynthetic membranes are used across a broad spectrum of industries, offering solutions to many environmental and engineering challenges. Some common applications include:
Landfill Liners: Geosynthetic membranes are used in landfill construction to prevent the leakage of leachate into the surrounding environment. They create a barrier between waste and the underlying soil or groundwater.
Water and Wastewater Management: Membranes are used in the construction of reservoirs, ponds, and canals to prevent water loss and contamination. They also play a crucial role in wastewater treatment plants to contain hazardous substances.
Mining: In the mining industry, geomembranes are used for heap leach pads, tailing ponds, and mining containment applications to protect surrounding ecosystems from toxic substances.
Pond and Lagoon Liners: Geosynthetic membranes are commonly used to line ponds, lagoons, and other water containment structures to prevent leakage and contamination.
Roofing Systems: EPDM and PVC membranes are popular choices for flat and low-slope roofing systems, offering excellent waterproofing and durability.
Coastal and River Protection: Geosynthetic membranes are used in coastal engineering to prevent erosion and protect riverbanks from water flow impacts.
Conclusion
Geomembranes are a crucial element in modern construction, environmental protection, and industrial applications. Their ability to provide a durable, waterproof barrier, coupled with their ease of installation and versatility, makes them indispensable in many industries. While they do have some drawbacks, such as susceptibility to punctures and environmental concerns, their benefits far outweigh the negatives. By understanding the manufacturing process, types, and potential applications, businesses and engineers can make informed decisions when selecting geomembranes for their projects.

897.webp)
942.webp)
237.webp)