by Lucia-Haoyang Environment
Nonwoven geotextile is a type of geosynthetic material extensively used in civil engineering applications. It is manufactured from natural or synthetic polymers such as plastics, chemical fibers, and synthetic rubbers. These materials are processed into various forms and placed within, on, or between soil layers to reinforce or protect the soil. This article delves into the definition, classification, and production processes of nonwoven geotextiles, with a focus on two primary types: long-filament needle-punched nonwoven geotextile and staple fiber needle-punched nonwoven geotextile.
I. Definition
Nonwoven geotextile represents a class of materials that are not woven, knitted, or otherwise formed using traditional textile techniques. Instead, they are produced through processes like needle-punching, spray bonding, or thermal bonding. These materials offer unique properties such as high tensile strength, water permeability, and durability, making them ideal for various soil engineering applications.
II. Performance Characteristics
Performance Characteristic | Description & Specifications |
Tensile Strength | High tensile strength to withstand loads. Typically measured in kN/m. Example: 200-500 kN/m forfilament needle-punched nonwoven geotextiles. |
Tear Resistance | Resistance to tearing, ensuring durability. Measured in kN. Example: ≥40 kN for certain types of nonwoven geotextiles. |
Elongation at Break | Ability to stretch without breaking, providing flexibility. Typically 10%-30%. |
Permeability | Allows water to flow through, controlled by pore size. Measured in cm/s or permeability coefficient. Example: ≥0.1 cm/s for certain applications. |
Filtration | Retains soil particles while allowing water to pass. Effective particle retention size (EPS) varies based on application. |
Chemical Stability | Resistant to acids, alkalis, and biological degradation. Tested according to standard methods, such as ASTM or ISO. |
Aging Resistance | Maintains performance over time, resistant to UV and weathering. Tested for durability in accelerated aging tests. |
III. Product Classification
Haoyang mainly uses needle-punched method to produce non-woven fabrics, which can be broadly classified into two categories based on their fiber length: short staple fiber needle-punched nonwoven geotextile and filament needle-punched nonwoven geotextile.
1. Short Staple Fiber Needle-Punched Nonwoven Geotextile
Production Raw Materials:
Polyester(PET)/polypropylene(PP) staple fibers with a denier of 6-12 and a length of 54-64mm.
Production Equipment:
l Fiber opening machines
l Combing machines
l Crosslapper
l Needle-punching machines
Production Process:
(1) Fiber Opening and Combing: Fibers are opened and cleaned to remove impurities. They are then combed to align them.
(2) Crosslapping: Fibers are laid in a uniform layer on a conveyor belt.
(3) Needle-Punching: Fibers are interlocked using needles to form a stable structure.
(4) Finishing: The product undergoes additional treatments like calendaring or coating to enhance its properties.

Staple fiber needled geotextile production equipment
Product Specifications:
l Weight: Ranges from 80g/m² to 800g/m², with heavier materials offering higher tensile strength and durability.
l Width: Typically ranges from 1m to 6m, customizable based on customer requirements.
l Length: Customizable, commonly produced in rolls of 6 meters by 50 meters for ease of transportation and cost savings.
l Tensile Strength: Measured in kN/m, with values ranging from 3 kN/m to 40 kN/m, depending on the application and material specifications.
Product Code Representation:
The product code for short-staple needle-punched nonwoven geotextiles follows a standardized representation to facilitate identification and specification. The code typically consists of four parts, separated by hyphens, as follows:
Part | Description | Example |
1 | Product Name | SNG (Short Staple Needle-punched Geotextile) |
2 | Fiber Type | PET (Polyester), PP (Polypropylene), PA (Polyamide/Nylon), PV (Polyvinyl), PE (Polyethylene); for mixed fibers, each component is listed separated by a slash (/) |
3 | Tensile Strength | Measured in kN/m |
4 | Width | Measured in meters (m) |
Example Product Codes:
(1) SNG-PET-10-6: Represents a polyester (PET) short-staple needle-punched nonwoven geotextile with a tensile strength of 10 kN/m and a width of 6 meters.
(2) SNG/C-PET/PP-15-4: Represents a composite (C) short-staple needle-punched nonwoven geotextile made of polyester (PET) and polypropylene (PP) fibers, with a tensile strength of 15 kN/m and a width of 4 meters.
*In addition to the basic specifications and product code, customers can also specify other requirements such as thickness, color, and packaging.
Properties and Applications:
Short fiber needle punched nonwoven geotextile is a type of geomaterial produced through a needle-punching process using short fibers. This material boasts high strength, excellent tensile properties, corrosion resistance, and good filtration performance. It forms a three-dimensional structure by intertwining, fusing, and fixing short fibers on a needle-punching machine.
Application Areas:
(1) Slope Protection in Landscaping: It serves as a slope protection material, effectively preventing soil erosion and protecting the soil from being washed away. For instance, laying this material on a hillside is akin to dressing the earth in armor, which is both aesthetically pleasing and practical.
(2) Road Construction: It can be used as a roadbed reinforcement material, enhancing the carrying capacity and stability of roads. This allows for more durable roads, reducing the frequency of maintenance and repairs, and saving considerable time and money.
(3) Water Conservancy Projects: It acts as an anti-seepage material, preventing water infiltration and leakage. It functions like an invisible barrier, safeguarding our water resources and ensuring the proper operation of water conservancy projects.
2. Long Filament Needle-Punched Nonwoven Geotextile
Production Raw Materials:
Primarily polyester. (Our company chooses PET chips produced by Sinopec, with high quality and stability)
Production Equipment:
l Extrusion machines
l Spinning and stretching equipment
l Needle-punching machines
661220.webp)
Filament spunbond and needlepunched nonwoven geotextiles production equipment
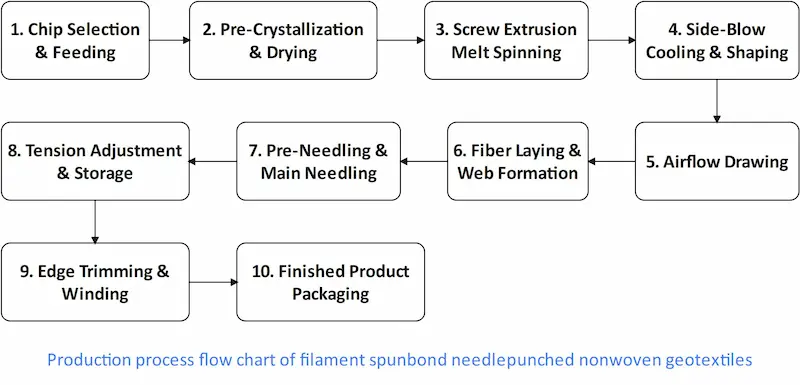
Production Process:
(1) Polymer Melting and Spinning: The polymer is heated and melted, then spun into continuous filaments.
(2) Drawing and Lay-up: Filaments are stretched and laid in a uniform manner on a conveyor belt.
(3) Needle-Punching: While the filaments are still slightly tacky, they are needle-punched to consolidate the structure.
(4) Finishing: The material is cooled and trimmed to the desired specifications.
Product Specifications:
l Weight: Ranges from 110g/m² to 800g/m², with heavier materials offering higher tensile strength and durability.
l Width: Typically ranges from 1m to 6.4m, customizable based on customer requirements.
l Length: Customizable, commonly produced in rolls for ease of transportation and cost savings.
l Tensile Strength: Measured in kN/m, with values ranging from 5 kN/m to 60 kN/m, depending on the application and material specifications.
Product Code Representation:
The product code for short-staple needle-punched nonwoven geotextiles follows a standardized representation to facilitate identification and specification. The code typically consists of five parts, separated by hyphens, as follows:
Part | Description | Example |
1 | Fiber Type | PET(Polyester), PP(Polypropylene) |
2 | Tensile Strength | Measured in kN/m |
3 | Width | Measured in meters (m) |
4 | Nominal Mass per Unit Area | Mass of the fabric per unit area. Measured in grams per square kilometer (g/m²) |
5 | Thickness | Measured in millimeters (mm) |
Example Product Codes:
(1) PET-15-4.5-290-1.6: it represents that the fabric is made of polyester fibers, has a nominal tensile strength of 15 kN/m, a width of 4.5 meters, a mass per unit area of 290 grams per square meter, and a thickness of 1.6 millimeters.
(2) PP15-5-200-2.0: it represents that the fabric is made of polypropylene fibers, has a nominal tensile strength of 15 kN/m, a width of 5 meters, a mass per unit area of 200 grams per square meter, and a thickness of 2.0 millimeters.
*In addition to the basic specifications and product code, customers can also specify other requirements such as thickness, color, and packaging.
IV. Properties and Standards:
Properties:
(1) Excellent Flexibility and Strength:
l It maintains robust strength and elongation both in dry and wet conditions.
l Typical specifications include a weight range of 100g to 1500g per square meter, with a breaking strength of 12.5KN/M for the most commonly designed variant (400g/m²).
(2) High Permeability and Filtration:
l It allows water to flow through while effectively retaining soil particles, preventing soil erosion and loss.
l The needle-punched structure creates a network of pores that facilitates drainage and gas ventilation within soil structures.
(3) Reinforcement and Stability:
l By enhancing the tensile strength and deformation resistance of soil, it contributes to the stability of building structures.
l For instance, in road, railway, and airport runway projects, it serves as a reinforcement layer to improve soil bearing capacity and prevent settlement and deformation.
(4) Stress Distribution:
l It distributes concentrated stresses, preventing soil from damage due to external forces and preventing the mixing of different soil and aggregate layers.
(5) Corrosion Resistance:
l Made from chemical fibers like polypropylene or polyester, it is resistant to acids, alkalis, corrosion, and insect infestation, ensuring long-term durability in various soil and water conditions.
(6) Lightweight and Easy to Handle:
l Its lightweight nature facilitates easy transportation, storage, and installation, reducing labor costs and improving construction efficiency.
Standards and Customization:
l The latest execution standard for this material is GB/T 17638-2017, although older standards like GB/T 17638-1998 are still used in some projects based on specific technical requirements.
l Standards can vary further, including large-scale, medium-scale, small-scale, and non-standard grades, as well as international standards like American standards and urban construction standards.
V. Functions and Applications of Nonwoven Geotextiles
Nonwoven geotextiles serve multiple purposes in civil engineering:
l Isolation: Prevents mixing of different soil materials and aggregates.
l Drainage: Facilitates water flow through the soil while retaining soil particles.
l Reinforcement: Enhances the tensile strength and deformation resistance of soil structures.
l Protection: Protects underlying structures from mechanical damage and chemical erosion.
l Filtration: Allows water to pass while retaining soil particles, preventing soil loss.
Application Fields:
(1) Hydropower, Highway, and Railway Engineering:
l Used as a reinforcement and drainage layer to enhance soil stability and prevent erosion in embankments, dams, and canal linings.
l Examples include reinforcing subgrades of roads and railways to improve load-bearing capacity.
(2) Ports and Airports:
l Employed in foundation reinforcement and drainage systems to ensure the stability of runways and port facilities.
(3) Tunnel and Coastal Reclamation Projects:
l Provides soil reinforcement and waterproofing in tunnel linings and coastal protection structures.
(4) Environmental Protection:
l Utilized in landfill liners, waste containment systems, and erosion control measures to protect the environment from contaminants.
(5) Sports Venues:
l Used in the construction of sports fields to provide drainage and stabilize the soil base, ensuring optimal playing conditions.
VI. Conclusion
Nonwoven geotextiles, particularly polyester staple fiber and long filament needle-punched nonwoven geotextiles, play a crucial role in modern civil engineering. Their unique properties and versatility make them indispensable in a wide range of applications. By understanding their production processes, material specifications, and functional characteristics, engineers can select the most suitable geotextile for each project, ensuring durability, safety, and cost-effectiveness.

897.webp)
942.webp)
237.webp)