Evaporation Pond
596149.webp)
An evaporation pond is an engineered structure used for the centralized treatment and management of liquid waste, aiming to enhance water resource recycling. Typically designed as a shallow and large water body, it facilitates the extraction of water from waste through natural evaporation, concentrating and solidifying the waste.
The impermeable layer of the evaporation pond is a critical design element. As evaporation ponds are commonly employed for storing liquid waste, inadequate impermeability measures on the pond bottom and sidewalls may lead to the leakage of harmful substances into groundwater or soil, causing environmental pollution. Therefore, to protect the surrounding ecosystems and water sources, an impermeable layer is of paramount importance.
The use of advanced technologies such as a double-layer geosynthetic impermeable lining can effectively reduce or prevent the seepage of water, ensuring the safe and efficient operation of the evaporation pond. The implementation of such impermeable layers helps prevent environmental pollution, safeguard water resources, and ensures proper treatment and disposal of waste.
Reclaimed Water Facility Evaporation Pond Project
395767.webp)
background:
Inner Mongolia Zhongmei Mengda New Energy Chemical Co., Ltd. is located in the Wushen Zhaoge Chemical Project Area of Uxin Banner, Ordos City, Inner Mongolia. The company has constructed a 500,000 tons per year engineering plastics project, including four main production sections: methanol-to-olefins, olefin separation, polypropylene, and polyethylene, along with relevant supporting facilities.
The evaporation pond, also known as a drying pond, utilizes natural processes such as sunlight and wind to allow the natural evaporation of water from the high-concentration brine at the end of the wastewater treatment process. This results in the concentration of solid crystals formed by oversaturation, which are then collected and sent to a secure landfill for final disposal, achieving zero wastewater discharge. As the high-concentration brine is classified as hazardous waste, the evaporation pond requires a double geosynthetic impermeable lining to ensure the operational safety of the impermeable system.
The project covers an area of approximately 30,000 square meters and is dedicated to the terminal treatment of wastewater.
The project selected our staple fiber needle-punched geofabric, HDPE geomembrane, and other impermeable products, with construction organized by our company. This effectively ensured the safety of groundwater in the project .
Our Solutions:
837106.webp)
The impermeable system structure of this evaporation pond adopts a double-layer composite design, and the function of each layer and the geosynthetic materials used, from bottom to top, are as follows:
1, Bentonite GCL: Effectively prevents the harm caused by uneven settlement to the HDPE geomembrane and serves as an auxiliary measure for impermeability and isolation.
2, Smooth HDPE geomembrane: The upper layer of HDPE membrane acts as the primary impermeable layer in the double-layer impermeable system. It is corrosion-resistant, aging-resistant, and provides excellent impermeable effects. The lower layer of HDPE geomembrane serves as the secondary impermeable layer, further enhancing impermeability.
3, Three-dimensional composite drainage net: Positioned between the upper and lower geomembranes, it is used to monitor the operation of the upper geomembrane.
4, Polypropylene short fiber needle-punched geotextile: Protects the geomembrane from external damage and serves as drainage, simultaneously.
Products Details
1, Sodium bentonite GCL
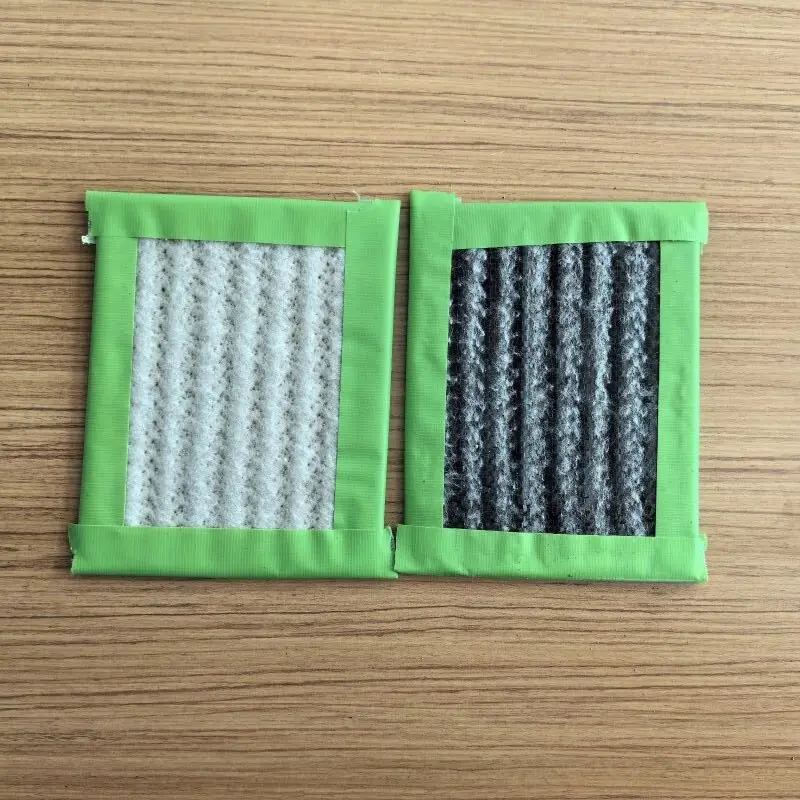

Sodium Bentonite Geosynthetic Clay Liner (GCL) is a type of geosynthetic material used in geotechnical and environmental engineering applications. It is composed of a layer of sodium bentonite clay sandwiched between two geotextile layers. The geotextile layers can be woven or non-woven and act as carriers for the bentonite, providing reinforcement and separation.
Functions of Sodium Bentonite GCL:
1), Impermeability: The primary function of Sodium Bentonite GCL is to provide an impermeable barrier. Bentonite clay has a high swelling capacity when it comes into contact with water. This swelling property helps in sealing potential pathways for water and other liquids, providing an effective barrier against seepage and leakage.
2), Environmental Containment: Sodium Bentonite GCL is commonly used in landfill liners, containment structures, and other environmental applications. It helps prevent the migration of contaminants from waste materials into the surrounding soil and groundwater.
3), Erosion Control: In civil engineering projects, Sodium Bentonite GCL can be used for erosion control purposes. The impermeable layer created by the swelling bentonite helps to reduce water infiltration, minimizing soil erosion and maintaining the stability of slopes and embankments.
4), Landfill Liners: GCLs are often used as part of composite liners in landfills to enhance the containment of leachate, preventing it from contaminating the surrounding environment.
5), Waterproofing: In certain construction applications, GCLs with sodium bentonite are used for waterproofing purposes, such as in the construction of reservoirs, ponds, or other water storage facilities.
2, Smooth HDPE geomembrane
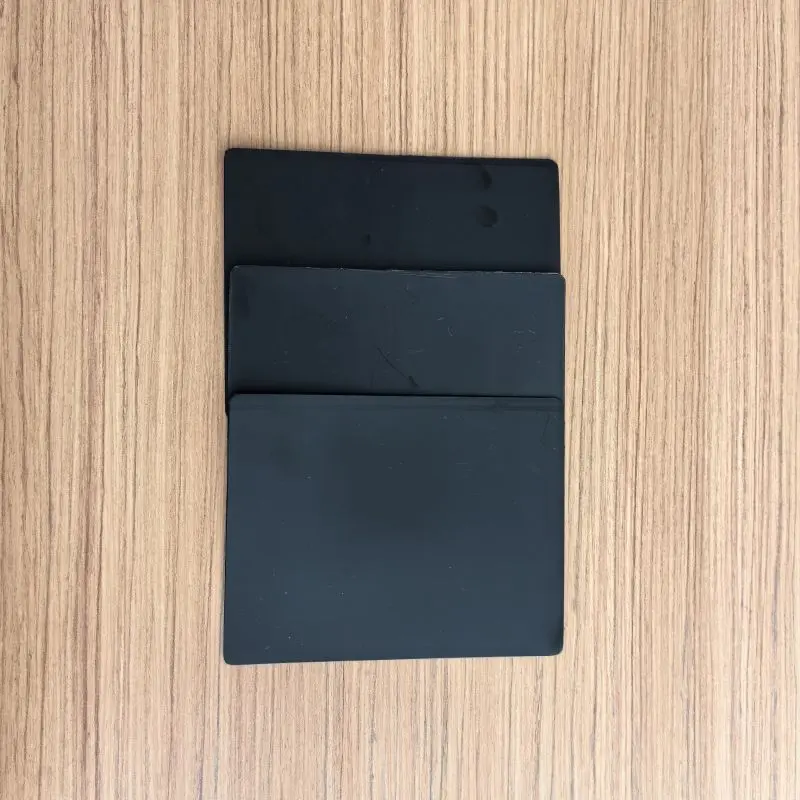

Smooth HDPE geomembrane is a geosynthetic material made of high-density polyethylene (HDPE) with a smooth surface. This type of geomembrane is commonly used in engineering, environmental protection, and water resource management. Its main functions include:
1), Primary Impermeable Layer: In waterproofing projects, smooth HDPE geomembrane is often used as the primary impermeable layer. Due to its high-density polyethylene composition, it exhibits excellent waterproofing properties, effectively preventing the penetration of water and protecting engineering structures, underground facilities, or liquid containment areas from water damage.
2), Corrosion Resistance and Aging Resistance: HDPE material is highly resistant to chemical corrosion, allowing the smooth HDPE geomembrane to maintain stability when in contact with various chemical substances. Additionally, HDPE has high resistance to aging, preserving its performance over extended periods of use.
3), Enhancing Impermeability: In some cases, smooth HDPE geomembrane may serve as a component of an impermeable system, working in conjunction with other geosynthetic materials (such as bentonite waterproof blankets) to collectively enhance the overall impermeability.
4), Used for Liquid Storage: Due to its superior impermeable performance, smooth HDPE geomembrane is frequently employed in liquid storage areas, ponds, wastewater treatment facilities, and other locations where liquid containment is critical to prevent leakage into the ground.
3, 3D composite drainage net
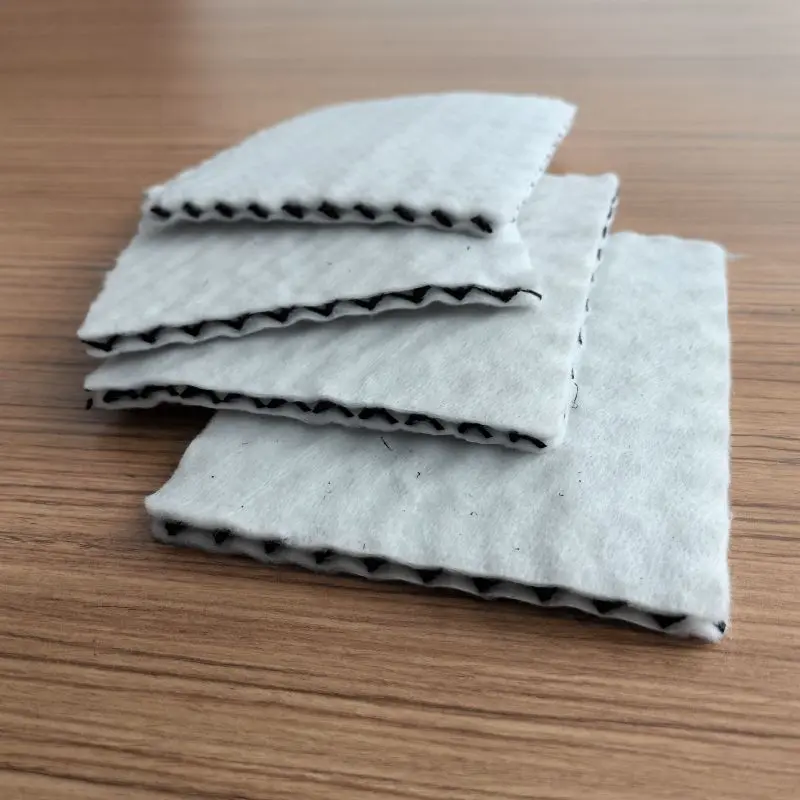

A 3D Composite Drainage Net is a three-dimensional composite drainage structure commonly used in civil and geotechnical engineering. It consists of multiple layers of different materials, including a three-dimensional drainage net and geosynthetic materials.
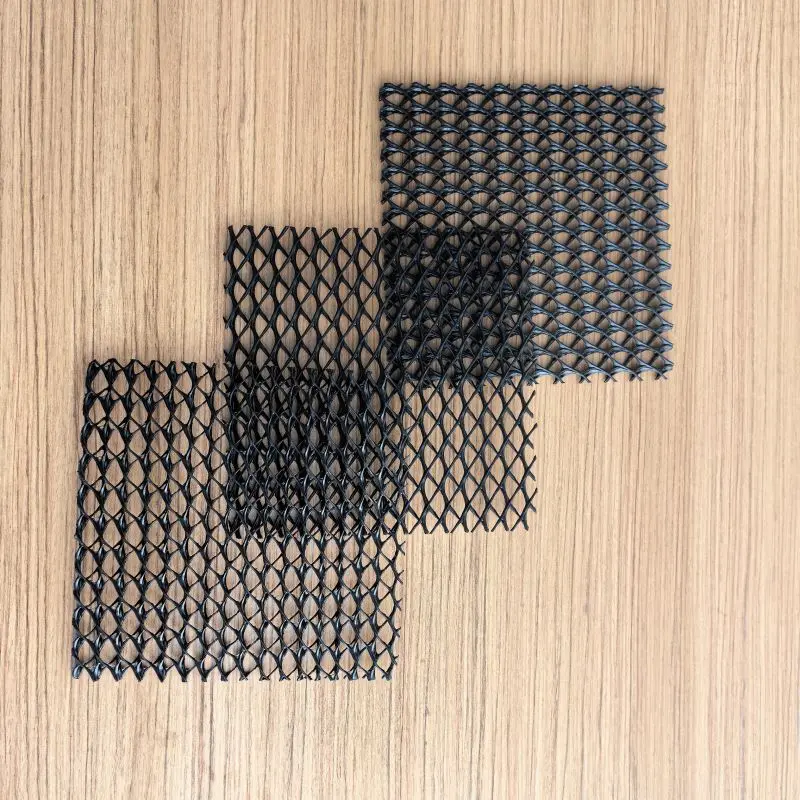
Its main functions include:
1), Drainage Function: The primary purpose of the 3D Composite Drainage Net is to facilitate drainage. With its unique three-dimensional structure, it effectively removes excess water in geotechnical engineering, reducing the groundwater level, preventing soil saturation, and avoiding liquefaction.
2), Enhancing Soil Stability: By facilitating drainage, the 3D Composite Drainage Net contributes to improving the stability of the soil. Preventing excessive water in the soil can reduce the weight of the soil, increase its shear strength, and enhance soil stability.
3), Monitoring the Operation of Impermeable Layers: In impermeable systems, the 3D Composite Drainage Net is typically positioned between upper and lower impermeable layers to monitor the operation of the upper impermeable layer. It helps engineers detect and address potential issues promptly, ensuring the effectiveness of the impermeable system.
4), Protecting Geomembranes: Placed beneath geomembranes, the 3D Composite Drainage Net serves to protect the geomembrane from damage caused by particles or sharp objects below.
5), Improving Foundation Soil Conditions: In civil engineering, the use of the 3D Composite Drainage Net can improve the drainage conditions of foundation soils, ensuring better engineering performance in moist conditions.
4,Polypropylene Staple Needle-Punched Geotextile
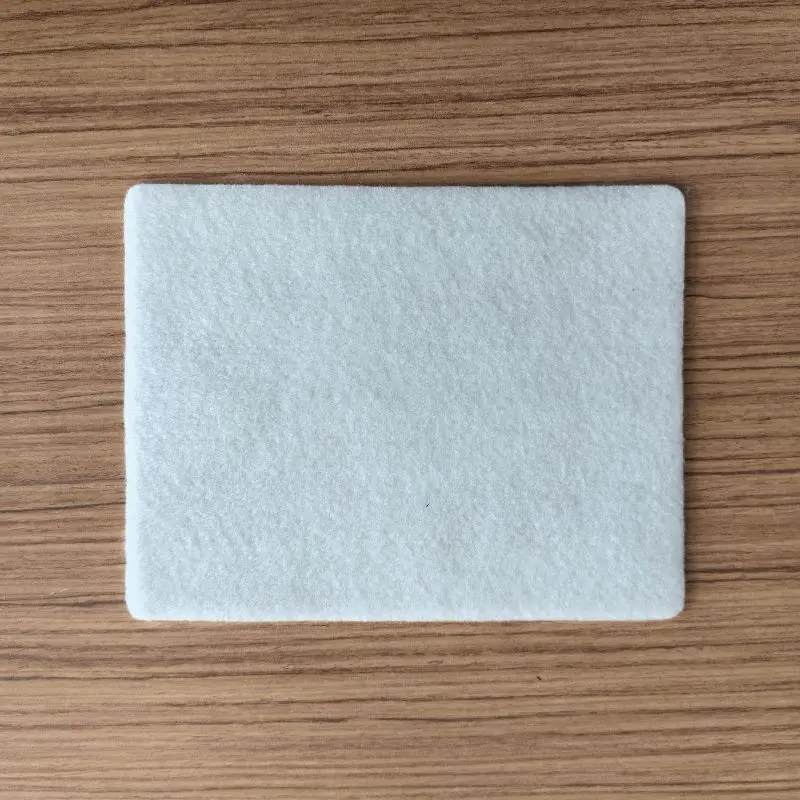

Polypropylene Staple Needle-Punched Geotextile is a geosynthetic material made from polypropylene short fibers through a needle-punching process. Its primary functions include:
1), Protective Role: Polypropylene short fiber needle-punched geotextile is commonly used to protect other geomembranes or impermeable layers in engineering, such as HDPE geomembranes, from external forces. It prevents damage from sharp objects, rocks, or other materials.
2), Water Conduction and Drainage: Due to its needle-punched structure, the geotextile's pores facilitate water flow, aiding in drainage and preventing water retention underground, thereby reducing the permeation pressure on the soil.
3),Soil Consolidation and Reinforcement: Polypropylene short fiber needle-punched geotextile can be used for the consolidation and reinforcement of soil. It provides structural support, slowing down soil settlement while increasing the tensile and compressive strength of the soil.
4), Environmental Protection: In certain environmental projects, such as land reclamation and desert greening, polypropylene short fiber needle-punched geotextile is utilized to improve soil structure, enhance soil fertility, and retain moisture.
5), Filtration Function: The fine fiber structure of polypropylene short fiber needle-punched geotextile is useful for filtering particles in the soil, preventing them from entering the geotechnical structure and maintaining the permeability of the geotextile.
FAQ
1. What is the purpose of using a double geosynthetic impermeable lining in an evaporation pond?
The double geosynthetic impermeable lining is employed to enhance the pond's impermeability, preventing the leakage of liquids and ensuring the containment of potentially hazardous materials. It provides an extra layer of protection against environmental contamination.
2. How does the double-layer composite structure of the impermeable lining work in an evaporation pond?
The double-layer composite structure typically consists of a combination of materials such as bentonite waterproof blankets and smooth HDPE geomembranes. This design aims to synergize the strengths of each layer, utilizing properties like swelling capacity and corrosion resistance to create a robust impermeable barrier.
3. What are the potential risks associated with not using a double geosynthetic impermeable lining in an evaporation pond?
Without a double impermeable lining, there is an increased risk of seepage and leakage, leading to groundwater contamination and environmental hazards. The pond may fail to effectively contain concentrated liquids, posing a threat to surrounding ecosystems.
4. How does the three-dimensional composite drainage net contribute to the effectiveness of the impermeable lining in an evaporation pond?
The three-dimensional composite drainage net helps in monitoring the performance of the upper impermeable layer. Positioned between the upper and lower layers, it facilitates drainage and aids in detecting any issues with the upper layer, ensuring the overall effectiveness of the impermeable system.
5. Is the use of a double geosynthetic impermeable lining a standard practice in evaporation pond construction?
Yes, it is a common industry practice. The use of a double geosynthetic impermeable lining is considered a best practice to provide a redundant and reliable barrier, minimizing the risk of leaks and ensuring compliance with environmental regulations.
(1)713.webp)
897.webp)
942.webp)
237.webp)