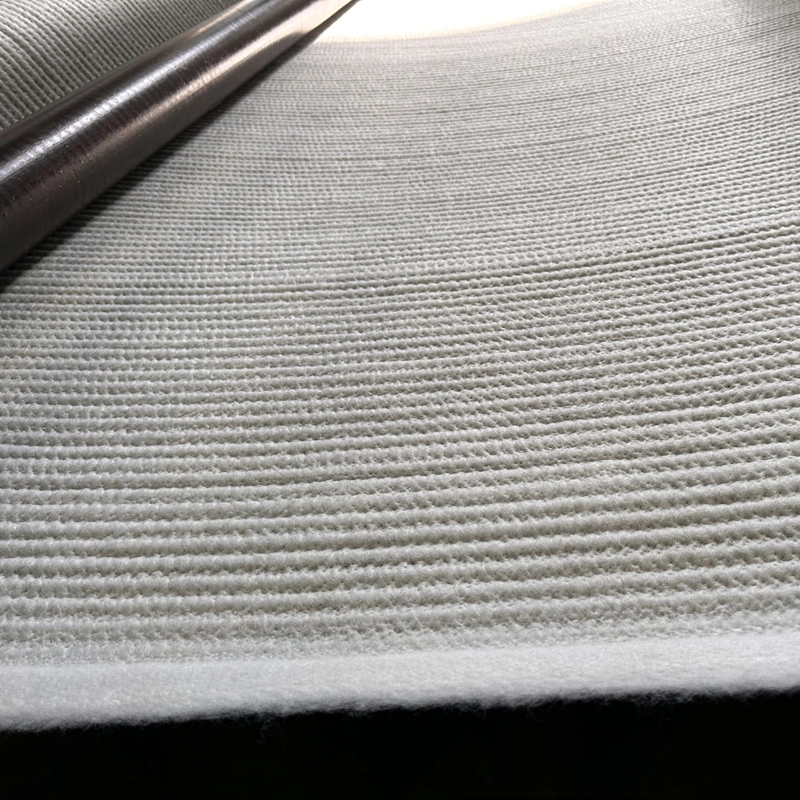
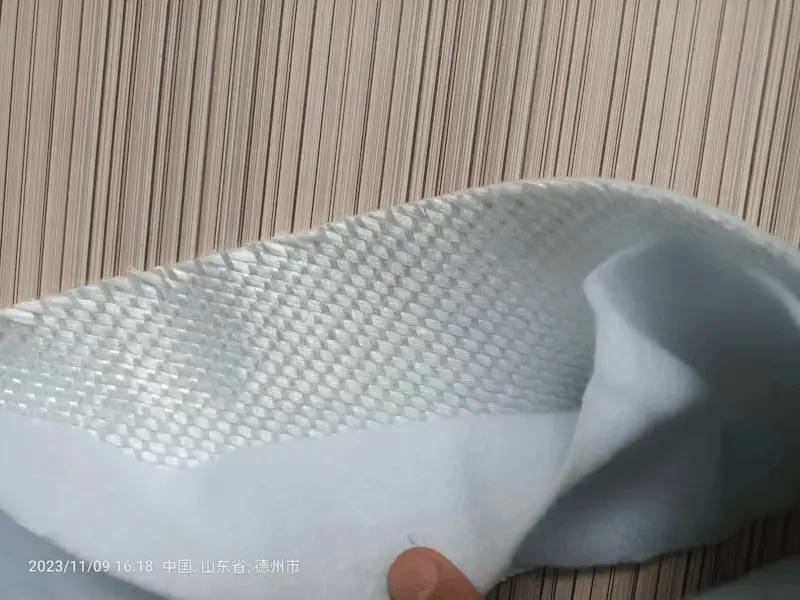
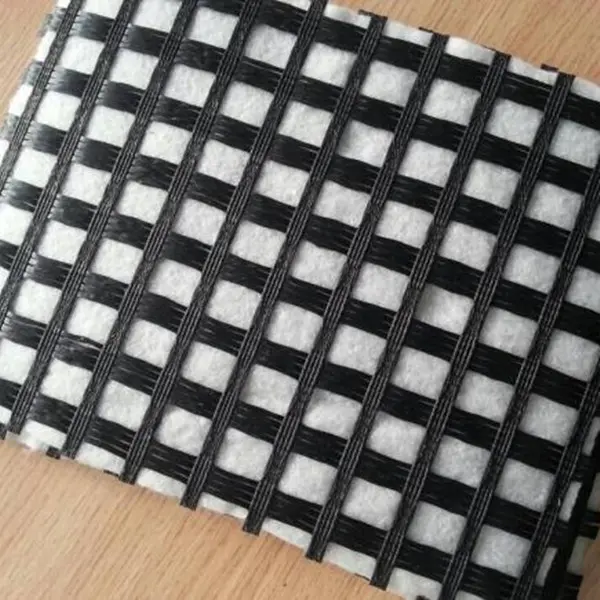
What is glass fiber composite geotextile?
Glass fiber composite geotextile is made of glass fiber as reinforcement material and is compounded with short fiber needle-punched non-woven fabric. Glass fiber composite geotextile is different from general woven fabric. The characteristic is that the intersection of warp and weft is not bent, and each is in a straight state. The two are tied firmly and evenly with binding wire, which bears external force and distributes stress. When the external force is applied to tear the material, the yarn will gather along the initial crack to increase the tear strength. When warp knitting is compounded, the warp knitting binding wire is used to repeatedly pass between the warp, weft yarn and the fiber layer of the short fiber needle-punched geotextile to weave the three into one. Therefore, the warp knitted composite geotextile has the characteristics of high tensile strength and low elongation, and also has the performance of needle-punched non-woven fabric. Therefore, the warp knitted composite geotextile is a kind of material that can be used for reinforcement, isolation and protection, and has good water collection and water separation. Because its solid matrix and pores are both continuous phases and become porous filtering effects, it is a multifunctional geocomposite material.
Specifications Table for Fiberglass Composite Geotextile
| Specification | Description |
|---|---|
| Material | Fiberglass mesh + Non-woven geotextile (polyester or polypropylene) |
| Weight | 150gsm - 800gsm (grams per square meter) |
| Width | 1m - 6m (custom widths available) |
| Length per Roll | 50m - 100m (varies with weight and thickness) |
| Fiberglass Mesh Size | 2.5mm x 2.5mm to 5mm x 5mm |
| Tensile Strength | ≥ 50 kN/m to 200 kN/m (depending on the weight and application) |
| Elongation at Break | ≤ 4% (low elongation for stability) |
| Temperature Range | -40°C to 100°C (-40°F to 212°F) |
| Water Permeability | High permeability, suitable for drainage and filtration applications |
| UV Resistance | UV-stabilized for extended outdoor use |
| Puncture Resistance | High resistance due to fiberglass reinforcement |
| Applications | Road reinforcement, retaining walls, slope stabilization, erosion control |
| Compliance | ISO 9001, ASTM standards for geotechnical applications |
| Color | Typically white, black, or grey |
| Durability | Designed for long-term use, up to 30 years in buried applications |
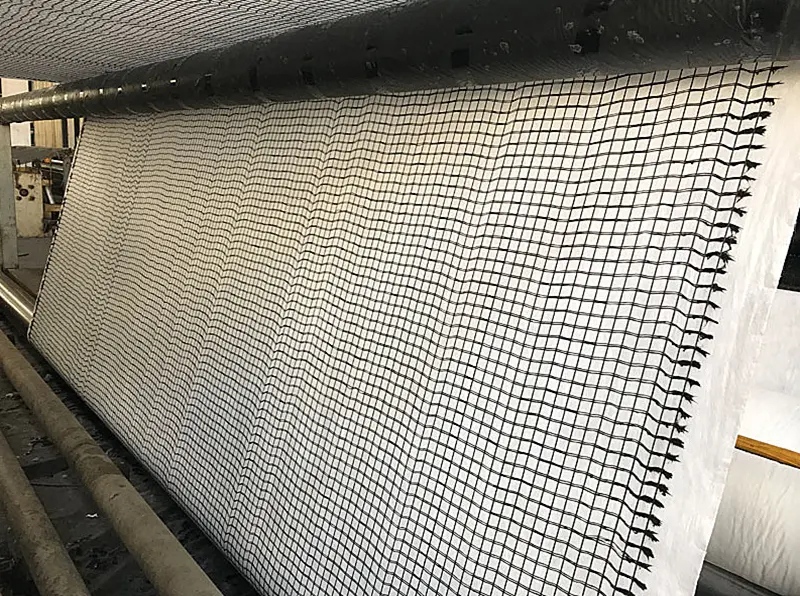

1. Features
1.1.High tensile strength:
Fiberglass grating has extremely high tensile strength and can effectively disperse and transfer tensile stress in the soil. It can provide stability in geotechnical structures with high stress and reduce soil deformation and settlement.
1.2.Excellent filtration performance:
The non-woven part has excellent water permeability and filtration, which can effectively prevent soil particles from being lost with the water flow while maintaining the smooth discharge of water. This is particularly important in water conservancy projects to prevent soil erosion and water accumulation.
1.3.Corrosion resistance:
Fiberglass grating itself has the characteristics of chemical corrosion resistance and can maintain its performance for a long time in acidic and alkaline soils and other harsh environments. This makes the material have a long service life in harsh environments such as chemical plants and landfills.
1.4.Lightweight and convenient construction:
The overall weight of the composite cloth is light, which is easy to transport and lay, and can be cut and adjusted according to the specific needs of the construction site to adapt to complex terrain conditions.
1.5.High temperature resistance:
Fiberglass has high temperature resistance and can maintain structural stability in high temperature environments, which is very important in some special projects.

2. Application Areas
2.1.Road and Railway Construction:
In the construction of road and railway infrastructure, fiberglass grid and non-woven composite fabrics are often used to strengthen the roadbed and prevent road settlement, cracking and other deformations. It can provide additional support and extend the service life of roads and railways.
2.2.Water Conservancy Project:
This composite material is widely used in water conservancy projects such as reservoirs, river embankments, and water diversion channels to prevent soil erosion, protect the stability of dams, and prevent leakage.
2.3.Landfill and Industrial Waste Sites:
In landfills and industrial waste treatment sites, fiberglass grid and non-woven composite fabrics are used to prevent the spread of harmful substances, while strengthening the structural stability of the site and preventing environmental pollution.
2.4.Soft Soil Foundation Treatment:
In the reinforcement of soft or muddy foundations, this composite material can provide additional support, improve the bearing capacity of the foundation, and prevent excessive settlement.
2.5.Tunnel and Underground Engineering:
In tunnels and other underground projects, fiberglass grid and non-woven composite fabrics are used to support the structure and provide drainage functions to prevent groundwater intrusion.
In summary, fiberglass grating and non-woven composite fabrics are widely used in various civil engineering projects due to their high strength, excellent filtration and drainage, and corrosion resistance, especially in situations where enhanced stability, leakage prevention, and soil erosion prevention are required.
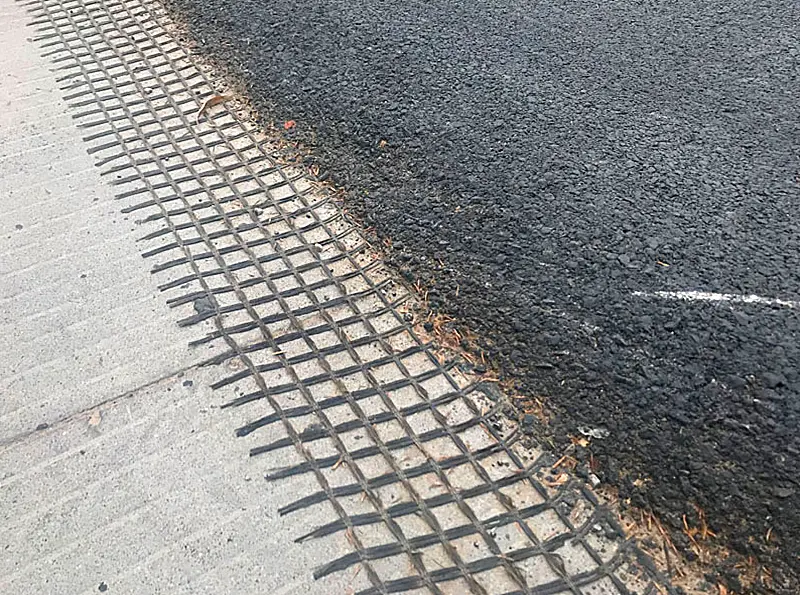

3. Test indicators
3.1.Tensile Strength:
Glass fiber grating part: Tensile strength is the most important mechanical indicator of glass fiber grating, which is usually tested in both longitudinal and transverse directions. The common test method is tensile test to determine the maximum bearing capacity of the material under stress.
Elongation at Break:
Elongation indicates the percentage of extension of the material during the stretching process. It is usually necessary to ensure that the elongation of the glass fiber grating is low to ensure that it maintains the stability of its shape when subjected to stress.
3.2.Peel Strength:
Test the bonding strength between the glass fiber grating and the non-woven fabric to ensure that the two materials will not separate during use, thereby maintaining the overall performance of the composite material.
3.3.Water Permeability:
The water permeability of the non-woven fabric part is its key performance. The permeability test is usually used to measure the water flow rate of the material under a certain pressure. This indicator is particularly important for the application of geotechnical materials in drainage and filtration.
3.4.Tear Resistance:
Measures the material's ability to resist tearing, especially during construction or under external forces. The tear resistance of the non-woven part is very important to avoid damage to the material during laying or use.
3.5.Durability:
Includes resistance to environmental factors such as ultraviolet rays, chemicals, temperature changes, etc. to ensure the long-term performance of the material in different environments.
These test indicators are usually carried out through standardized test methods, such as ASTM (American Society for Testing and Materials) or ISO (International Organization for Standardization) standards to ensure that the material meets the needs of a specific engineering project.
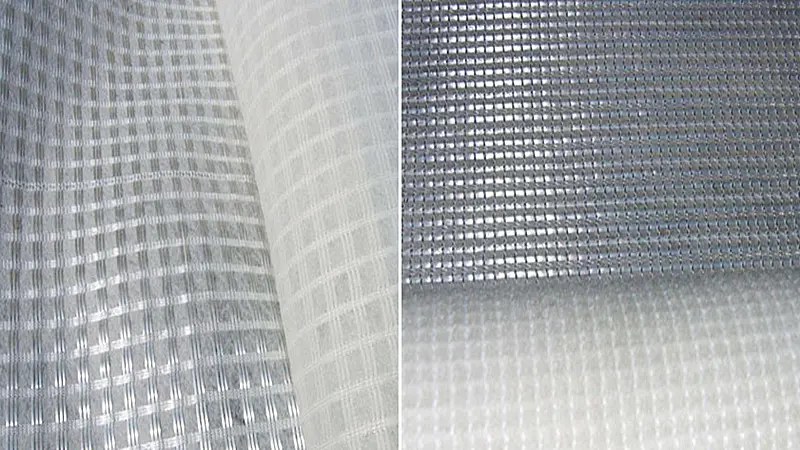
4. Minimum test index of fiberglass grille
No. | Item | Unit | Data | Remark | |
1 | Tensile Strength | Longitudinal tensile strength | KN/m | ≥50 | - |
Transverse tensile strength | KN/m | ≥50 | - | ||
2 | Elongation at Break | - | ≤ 4% | - | |
3 | Peel Strength | N/50mm | 100 | Peel strength between glass fiber grid and non-woven fabric | |
4 | Durability (UV aging) | - | ≥ 90% | 500 hours UV weathering test | |
5. Minimum testing index for non-woven fabrics
No. | Item | Unit | Data | Remark | |
1 | Mass per Unit Area | g/m² | ≥ 100 | - | |
2 | Water Permeability | cm/s | ≥ 10^-3 | - | |
3 | Tear Resistance | Vertical | N | ≥ 200 | - |
4 | Horizontal | N | ≥ 200 | - | |
5 | Thickness | mm | ≥ 1 | - | |

6. Minimum test indicators for composite materials
No. | Item | Unit | Data | Remark |
1 | Composite Tensile Strength | kN/m | ≥ 60 | The tensile strength of the composite material |
2 | Composite Peel Strength | N/50mm | ≥ 200 | Peel strength of composite materials |
Notes:
These minimum values are based on general industry standards and reference data, and actual values may vary depending on different product specifications and standards. When selecting and testing these materials, relevant international standards such as ASTM D6637 (tensile strength test of fiberglass grid) and ISO 10319 (wide strip tensile test of geosynthetics) should be followed.
Price List for Fiberglass Composite Geotextile
| Weight (gsm) | Tensile Strength (kN/m) | Roll Size | Factory Price (USD per Square Meter) | Factory Price (USD per Roll) | Application |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 150 gsm | 50 kN/m | 100m x 2m | $0.50 - $0.70 | $100 - $140 | Basic road reinforcement, soil separation |
| 200 gsm | 70 kN/m | 100m x 2m | $0.70 - $0.90 | $140 - $180 | Drainage systems, light slope stabilization |
| 300 gsm | 100 kN/m | 50m x 2m | $0.90 - $1.20 | $90 - $120 | Erosion control, retaining walls |
| 400 gsm | 150 kN/m | 50m x 2m | $1.20 - $1.50 | $120 - $150 | Heavy-duty road reinforcement, geotechnical projects |
| 600 gsm | 200 kN/m | 50m x 2m | $1.50 - $2.00 | $150 - $200 | Large-scale road and highway projects |
| 800 gsm | 200+ kN/m | 50m x 2m | $2.00 - $2.50 | $200 - $250 | Industrial applications, reinforced slopes |
Note: Prices may vary based on order quantity, location, and specific project requirements. Discounts may be available for bulk orders.
Haoyang Environmental Co., Ltd. is a company specializing in the production of geotechnical materials. It has more than 20 years of production experience and can provide free advice for any problems you encounter during the purchase and use of geotechnical materials. You can communicate with us at any time if you have any questions.
Email: sale2@hygeosynthetics.com
Monile: +8616615773081




503.webp)
759.webp)

