What is geomembrane
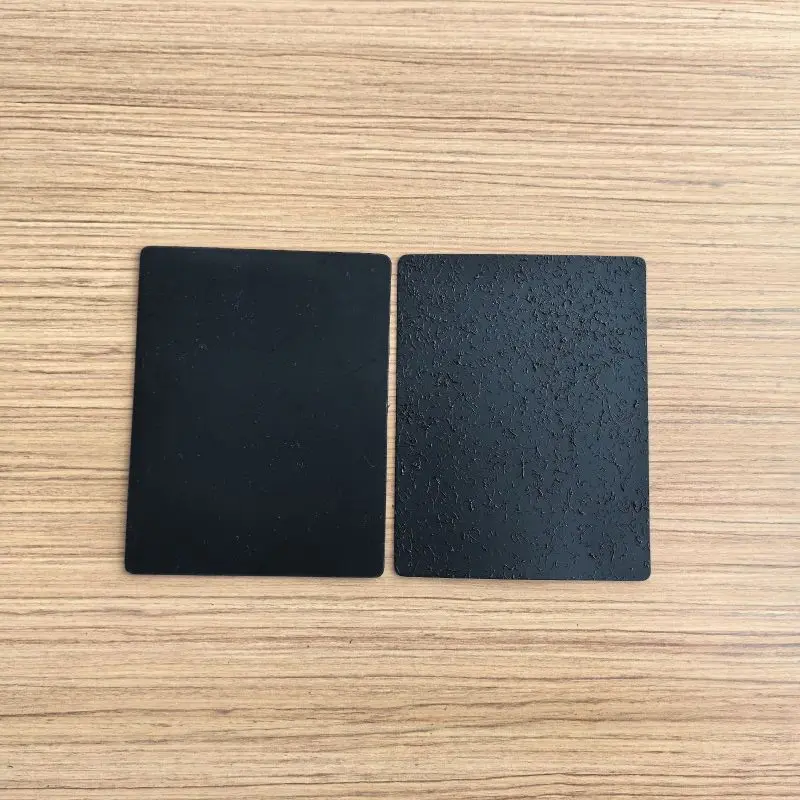

A geomembrane is a synthetic membrane liner or barrier used in various engineering applications to control the movement of fluids, gases, or contaminants. It is typically made from flexible synthetic materials such as high-density polyethylene (HDPE), polyvinyl chloride (PVC), or ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM). Geomembranes are commonly used in environmental containment systems, such as landfill liners, pond liners, and reservoirs, to prevent the migration of liquids or pollutants into the surrounding soil or groundwater. They are also employed in civil engineering projects for waterproofing structures like tunnels, dams, and canals. Geomembranes are chosen for their durability, flexibility, and resistance to chemical and environmental degradation.
Geomembranes play a critical role in various engineering applications, particularly in cold regions where environmental conditions can pose unique challenges. Selecting the appropriate geomembrane in such areas requires careful consideration of several factors to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Main functions of geomembrane
As the best waterproofing materials, the main functions of geomembranes include:
1, Containment: Geomembranes serve as impermeable barriers to prevent the migration of liquids, gases, or contaminants. They are commonly used in environmental containment applications such as landfill liners, pond liners, and wastewater treatment facilities to prevent leakage into the surrounding soil or groundwater.
2, Waterproofing: Geomembranes are used to provide waterproofing in civil engineering projects such as tunnels, dams, canals, and reservoirs. They help to prevent water infiltration and seepage, thereby protecting structures from water damage and maintaining their structural integrity.
3, Erosion Control: Geomembranes can be used as erosion control measures to stabilize slopes, embankments, and shorelines. By preventing soil erosion and sedimentation, they help to maintain the stability of the terrain and protect against erosion-related hazards.
4, Gas Barrier: In certain applications, such as landfill liners and containment systems for hazardous waste, geomembranes serve as barriers to prevent the escape of harmful gases, such as methane and volatile organic compounds (VOCs), into the atmosphere.
5, Linings for Agriculture: Geomembranes are used in agriculture for various purposes, including lining irrigation canals, reservoirs, and storage ponds to prevent water loss through seepage and evaporation. They can also be used in greenhouse construction to control soil moisture and prevent weed growth.
Overall, geomembranes play a crucial role in a wide range of engineering, environmental, and agricultural applications by providing effective containment, waterproofing, erosion control, and gas barrier solutions. In cold regions, the selection of geomembranes is crucial for ensuring the effectiveness and longevity of various engineering projects, including landfill liners, pond liners, and containment systems.
How to choose geomembranes for cold Regions
Understand geomembarnes application environmental conditions:
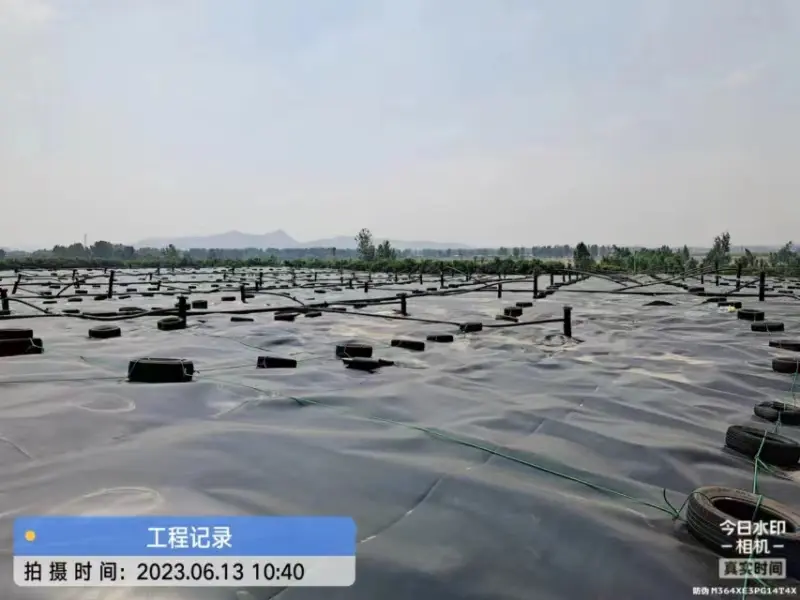

1, Temperature Extremes: Cold regions often experience significant temperature fluctuations, with sub-zero temperatures during winter months. Geomembranes selected for these areas must be able to withstand these extremes without compromising their integrity.
2, Freeze-Thaw Cycles: The repeated freezing and thawing of soil and water can exert considerable stress on geomembranes. Choosing a material with high flexibility and resistance to cracking is essential to mitigate the effects of freeze-thaw cycles.
Material Selection:
3, Low-Temperature Flexibility: Polyethylene (HDPE), ethylene are commonly used geomembrane materials suitable for cold regions due to their high flexibility at low temperatures.
UV Stability: In addition to cold resistance, UV stability is crucial, especially in areas with prolonged sunlight exposure during summer months. UV-resistant geomembranes can prevent degradation and prolong service life.
Thickness and Strength:
4, Thicker geomembranes offer increased puncture resistance and durability, which are especially important in cold regions where ground conditions may be harsh.
Consider the anticipated loads and stresses the geomembrane will be subjected to, including snow loads, ice pressure, and potential impacts from construction activities.
Installation and Seaming:
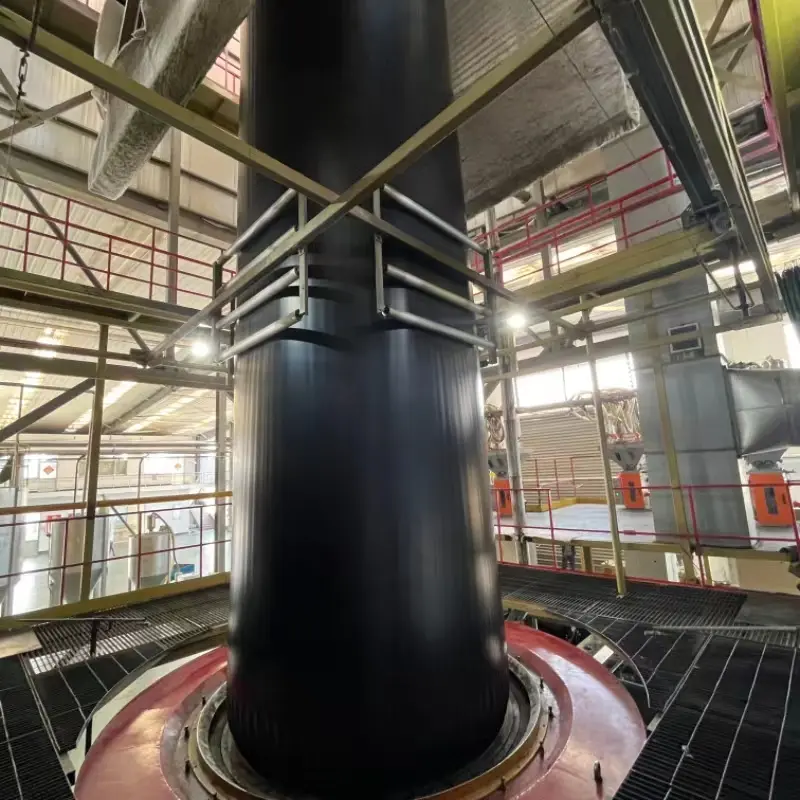

Cold Weather Installation: Specialized installation techniques may be required in colder temperatures to ensure proper seam fusion and adhesion. Heating elements or hot air blowers can be used to facilitate seam welding in low-temperature conditions.
1, Quality Assurance: Proper training and supervision of installation crews are essential to maintain seam integrity and minimize the risk of leaks or failures.
Long-Term Performance:
2, Durability Testing: Before selecting a geomembrane, review manufacturers' specifications and conduct independent testing to assess material properties and performance under cold conditions.
3, Consider Environmental Factors: Evaluate the potential impact of factors such as frost heave, ground settlement, and thermal expansion on the geomembrane system's long-term performance.
In construction under severe winter conditions, it is advisable for everyone to procure high-quality geomembranes. Opting for materials produced from new raw materials ensures a softer texture, better resistance to low temperatures, and eliminates issues like cracking or tearing upon slight force. These materials exhibit excellent tensile strength and elongation rate, ensuring stability across various geological and lower environmental conditions. They provide robust assurance for engineering quality.
FAQ
1, What factors should be considered when selecting geomembranes for cold regions?
Factors to consider include temperature extremes, freeze-thaw cycles, material flexibility, UV stability, and long-term performance under harsh environmental conditions.
2, Which materials are suitable for geomembranes in cold regions?
Polyethylene (HDPE), ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM), and reinforced polyethylene (RPE) are commonly used due to their high flexibility and resistance to low temperatures.
3, How does thickness and strength impact geomembrane performance in cold climates?
Thicker geomembranes offer increased puncture resistance and durability, which are essential for withstanding harsh conditions and potential impacts from snow loads and ice pressure.
4, What are the key considerations for installation and seaming of geomembranes in cold weather?
Specialized installation techniques may be required, such as using heating elements or hot air blowers to facilitate seam welding and ensure proper adhesion in low-temperature conditions.
5, How can engineers ensure the long-term performance of geomembranes in cold regions?
Conducting durability testing, evaluating environmental factors like frost heave and thermal expansion, and selecting geomembranes with proven performance under cold conditions are essential steps to ensure long-term effectiveness.

897.webp)
942.webp)
237.webp)