What is Geogrid?
A geogrid is a geosynthetic material used primarily for reinforcing soils, enhancing the stability of earth structures, and providing a solid foundation for various construction projects. Geogrids are typically made from polymers like polypropylene (PP), high-density polyethylene (HDPE), or polyester (PET). They consist of a grid-like structure with apertures (open spaces) that allow soil or aggregate to pass through and interlock, improving load distribution and preventing soil movement.
Features of Geogrid
High Tensile Strength: Geogrids provide excellent resistance to tension, making them ideal for stabilizing weak soils.
Lightweight and Flexible: They are easy to transport and install, reducing construction time and labor costs.
Open Grid Structure: The open apertures allow for soil interaction and interlocking, which provides better load distribution and enhances stability.
UV and Chemical Resistance: Geogrids made from materials like HDPE or polypropylene are resistant to UV radiation and chemical exposure, which extends their durability in harsh environmental conditions.
Corrosion and Rust Resistance: Since geogrids are typically made from polymeric materials, they do not rust or corrode, even in moist or corrosive environments.
Benefits of Using Geogrid
Improved Soil Stability: Geogrids help reinforce weak soils by distributing loads more evenly, preventing soil displacement, and reducing the risk of deformation or collapse.
Increased Load-Bearing Capacity: By interlocking with the soil, geogrids improve the overall load-bearing capacity of the structure, reducing the thickness of aggregate layers needed for roads or embankments.
Cost-Effective: Using geogrids can reduce the amount of earth material needed, decrease construction time, and minimize maintenance costs due to better long-term stability.
Erosion Control: Geogrids help control soil erosion on slopes, embankments, and riverbanks by reinforcing the soil and allowing vegetation to grow through the apertures.
Extended Project Lifespan: Structures reinforced with geogrids tend to last longer due to their enhanced stability and durability, reducing the need for repairs or replacements.
Environmental Sustainability: Geogrids can reduce the need for large quantities of soil or rock in construction projects, minimizing environmental impact and preserving natural resources.
Uses of Geogrid
Road Construction:
Geogrids are commonly used in road construction to reinforce road bases and subgrades, ensuring they can withstand heavy traffic loads and preventing cracking or rutting. Biaxial and triaxial geogrids are particularly suited for this purpose.
Retaining Walls:
Uniaxial geogrids are used in retaining wall systems to reinforce the soil behind the wall, preventing the soil from collapsing and providing structural integrity.
Slope Stabilization:
Geogrids help stabilize steep slopes and embankments by providing a reinforced foundation, preventing landslides and erosion.
Railways:
Geogrids are often used in railway construction to stabilize the ballast layer, ensuring the rails remain stable under heavy loads and reducing the need for frequent maintenance.
Erosion Control:
In riverbanks, coastal areas, and slopes, geogrids are used to prevent soil erosion, particularly in areas subject to water runoff or wind erosion.
Landfills:
In landfill applications, geogrids are used to reinforce waste containment systems, ensuring the stability of the landfill and preventing structural failures.
Parking Lots and Driveways:
Geogrids are used in the construction of parking lots and driveways to improve load distribution and prevent sinking or cracking under heavy loads.
Bridges and Abutments:
Geogrids provide support in bridge construction by stabilizing the earth beneath the structure and reducing the risk of soil displacement over time.
Geogrids are a versatile, cost-effective solution for reinforcing soil and improving the stability of a wide range of construction projects. Their ability to increase load-bearing capacity, control erosion, and improve the durability of roads, retaining walls, slopes, and embankments makes them an essential material in civil engineering. With features like high tensile strength, resistance to environmental factors, and ease of installation, geogrids contribute significantly to the sustainability and longevity of modern infrastructure.
Types of geogrid, Specifications and Prices list
Geogrids are geosynthetic materials used in construction, especially in applications involving soil stabilization, reinforcement, and retaining walls. They are made of polymers such as polypropylene, polyethylene, or polyester, and are used to reinforce soils and similar materials. There are several types of geogrids, categorized based on their manufacturing process, materials, and applications. Below are the main types of geogrids:
1. Uniaxial Geogrid
Description: Uniaxial geogrids are designed to resist tension in one direction, typically along their length.
Manufacturing: These geogrids are made by stretching the polymer in a single direction, creating high tensile strength in that direction.
Applications: Used mainly for soil reinforcement, retaining walls, and slope stabilization where the primary stress is in one direction.
Key Features:
High tensile strength in one direction.
Excellent durability for long-term reinforcement.
Often used in retaining wall construction and embankments.

Size Specifications Table
| Specification | Details |
|---|---|
| Aperture Size | 25 mm - 100 mm |
| Width | 1 m - 6 m |
| Roll Length | 50 m - 200 m |
| Thickness | 1 mm - 3 mm |
| Material | HDPE/PP |
Technical Specifications Table
| Specification | Details |
|---|---|
| Tensile Strength | 40 kN/m - 200 kN/m |
| Elongation | ≤10% |
| Durability | High resistance to UV radiation |
| Application | Retaining walls, slopes |
Price Table
| Tensile Strength | Price (USD/m²) |
|---|---|
| 40 kN/m | $1.50 - $2.00 |
| 100 kN/m | $2.50 - $3.50 |
| 150 kN/m | $3.50 - $4.50 |
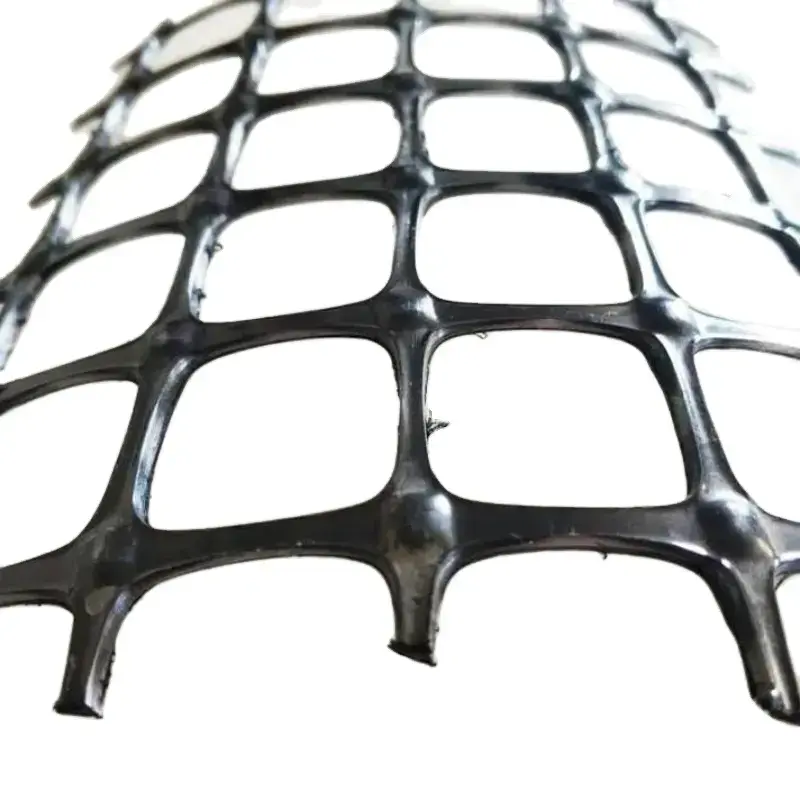
2. Biaxial Geogrid
Description: Biaxial geogrids are designed to resist tension in two directions: both lengthwise and crosswise.
Manufacturing: These geogrids are produced by stretching the material in both the machine direction (MD) and the cross-machine direction (CMD).
Applications: Commonly used in road construction, base reinforcement, and foundations where support in multiple directions is required.
Key Features:
Equal tensile strength in both directions.
Used to distribute loads over a wider area.
Provides effective stabilization for road bases and subgrades.

Size Specifications Table
| Specification | Details |
|---|---|
| Aperture Size | 20 mm - 80 mm |
| Width | 1 m - 5 m |
| Roll Length | 50 m - 100 m |
| Thickness | 0.5 mm - 2.5 mm |
| Material | PP/HDPE |
Technical Specifications Table
| Specification | Details |
|---|---|
| Tensile Strength | 20 kN/m - 100 kN/m |
| Elongation | ≤13% |
| Flexibility | High |
| Application | Road construction, embankments |
Price Table
| Tensile Strength | Price (USD/m²) |
|---|---|
| 20 kN/m | $1.00 - $1.50 |
| 50 kN/m | $1.50 - $2.50 |
| 100 kN/m | $2.50 - $3.50 |
3. Triaxial Geogrid (Triangular Geogrid)
Description: Triaxial geogrids, also known as triangular geogrids, offer multi-directional stability due to their unique triangular structure.
Manufacturing: These geogrids are manufactured with triangular apertures, providing more efficient load distribution across a wider range of angles.
Applications: Suitable for road foundations, pavement stabilization, and general soil reinforcement.
Key Features:
Provides multi-directional reinforcement.
Enhances soil stability by distributing loads evenly.
Ideal for roads, railways, and industrial pavements.
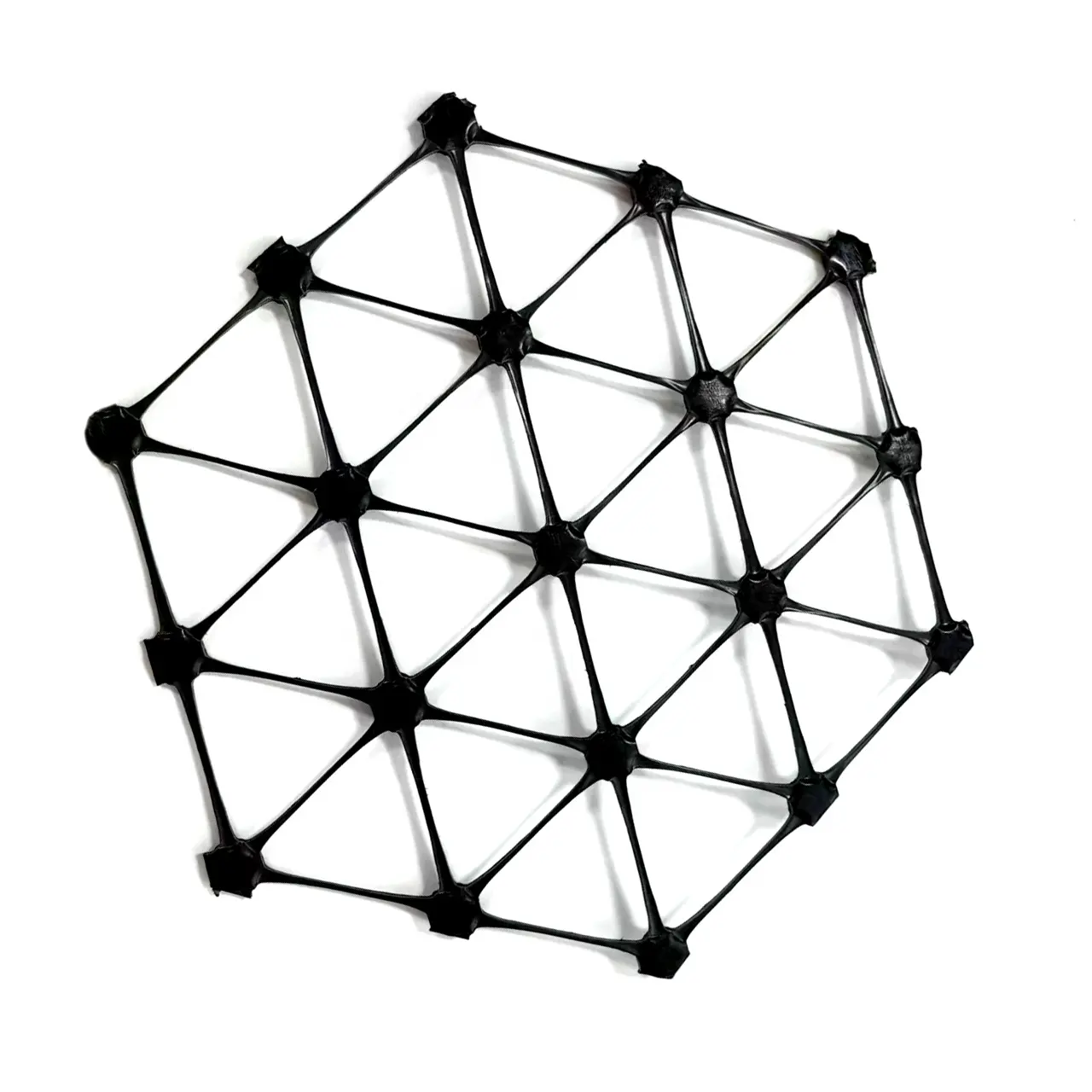
Size Specifications Table
| Specification | Details |
|---|---|
| Aperture Size | 30 mm - 100 mm |
| Width | 1 m - 5 m |
| Roll Length | 30 m - 100 m |
| Thickness | 1 mm - 3 mm |
| Material | PP/HDPE |
Technical Specifications Table
| Specification | Details |
|---|---|
| Tensile Strength | 40 kN/m - 120 kN/m |
| Elongation | ≤12% |
| Application | Road base reinforcement |
| Load Distribution | Multi-directional |
Price Table
| Tensile Strength | Price (USD/m²) |
|---|---|
| 40 kN/m | $1.80 - $2.50 |
| 80 kN/m | $2.50 - $3.50 |
| 120 kN/m | $3.50 - $4.50 |
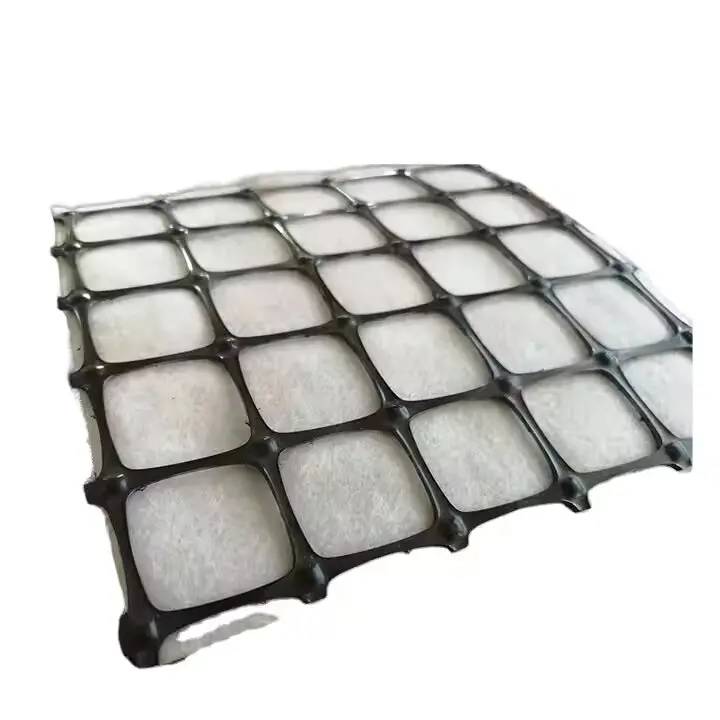
4. Extruded Geogrid
Description: Extruded geogrids are manufactured by stretching a flat sheet of polymer material (such as polyethylene or polypropylene) to create a grid pattern.
Manufacturing: This method involves extrusion and stretching, resulting in a product with strong junctions and high tensile strength.
Applications: Widely used in road construction, embankments, and landfill reinforcement.
Key Features:
High junction strength.
Suitable for load-bearing applications.
Provides long-term soil stabilization.

Size Specifications Table
| Specification | Details |
|---|---|
| Aperture Size | 20 mm - 60 mm |
| Width | 1 m - 4 m |
| Roll Length | 50 m - 100 m |
| Thickness | 1 mm - 2.5 mm |
| Material | HDPE/PP |
Technical Specifications Table
| Specification | Details |
|---|---|
| Tensile Strength | 30 kN/m - 150 kN/m |
| Elongation | ≤15% |
| Durability | UV resistance |
| Application | Roads, embankments, drainage |
Price Table
| Tensile Strength | Price (USD/m²) |
|---|---|
| 30 kN/m | $1.50 - $2.00 |
| 100 kN/m | $2.00 - $3.50 |
| 150 kN/m | $3.00 - $4.00 |
5. Woven Geogrid
Description: Woven geogrids are made by weaving polymer fibers (usually polyester) into a grid-like structure.
Manufacturing: These geogrids are produced by interlacing yarns or fibers to form a continuous grid.
Applications: Typically used in applications requiring high tensile strength, such as retaining walls and embankment reinforcement.
Key Features:
High tensile strength and durability.
Flexible and resistant to soil abrasion.
Often used in both temporary and permanent construction applications.
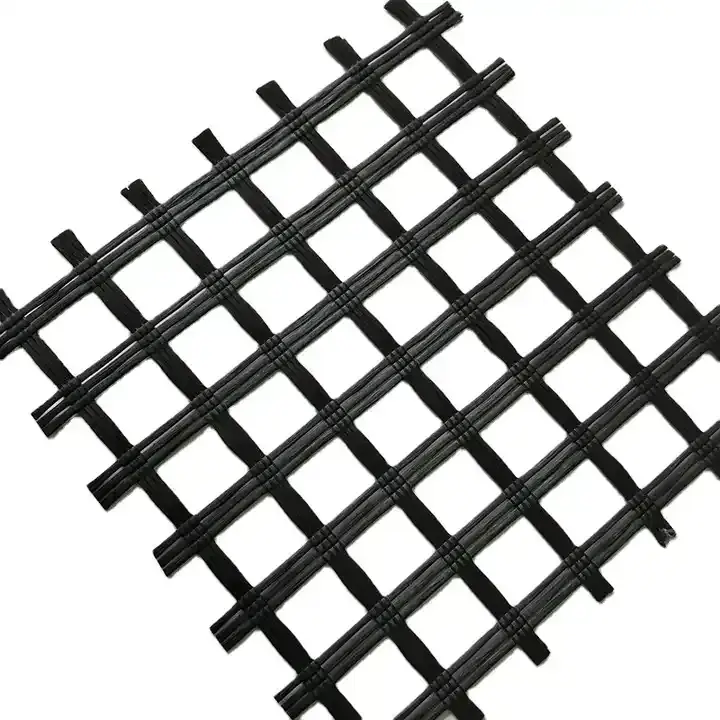
Size Specifications Table
| Specification | Details |
|---|---|
| Aperture Size | 25 mm - 100 mm |
| Width | 1 m - 6 m |
| Roll Length | 50 m - 100 m |
| Thickness | 1 mm - 3 mm |
| Material | Polyester, PP |
Technical Specifications Table
| Specification | Details |
|---|---|
| Tensile Strength | 50 kN/m - 300 kN/m |
| Elongation | ≤10% |
| Durability | High resistance to soil abrasion |
| Application | Heavy loads, reinforcement |
Price Table
| Tensile Strength | Price (USD/m²) |
|---|---|
| 50 kN/m | $2.00 - $2.50 |
| 150 kN/m | $3.00 - $4.00 |
| 300 kN/m | $4.00 - $6.00 |
6. Knitted Geogrid
Description: Knitted geogrids are made by knitting polymeric materials, like polyester, to form a grid structure.
Manufacturing: These are made by combining knitted yarns with a protective coating to improve durability and performance.
Applications: Commonly used in soil reinforcement applications where high tensile strength is required.
Key Features:
Lightweight and flexible.
High tensile strength in both directions.
Ideal for reinforcing retaining walls, embankments, and foundations.
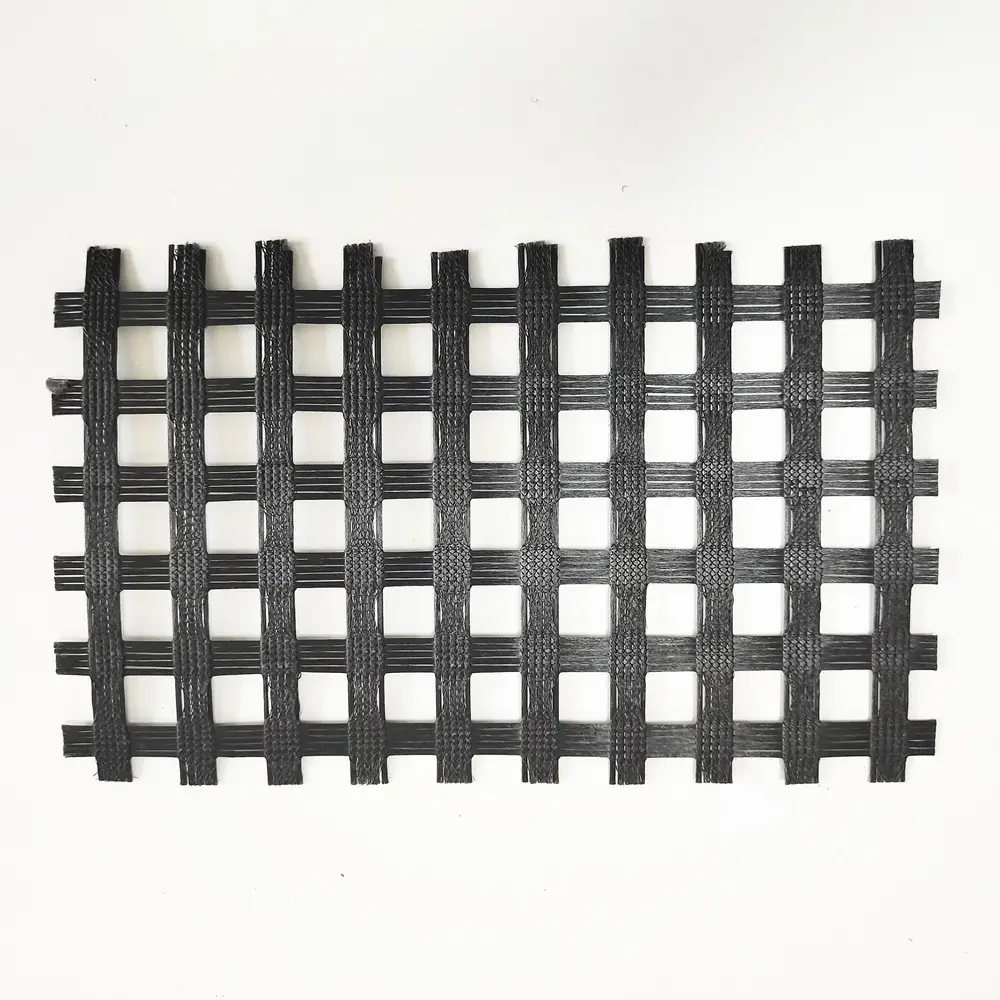
Size Specifications Table
| Specification | Details |
|---|---|
| Aperture Size | 20 mm - 60 mm |
| Width | 1 m - 5 m |
| Roll Length | 50 m - 100 m |
| Thickness | 1 mm - 2.5 mm |
| Material | Polyester, PP |
Technical Specifications Table
| Specification | Details |
|---|---|
| Tensile Strength | 30 kN/m - 200 kN/m |
| Elongation | ≤12% |
| Flexibility | High |
| Application | Foundations, soil stabilization |
Price Table
| Tensile Strength | Price (USD/m²) |
|---|---|
| 30 kN/m | $1.50 - $2.50 |
| 100 kN/m | $2.50 - $3.50 |
| 200 kN/m | $3.50 - $4.50 |
7. Coated Geogrid
Description: Coated geogrids are either woven or knitted geogrids that are coated with a material such as PVC or polyethylene for enhanced durability.
Manufacturing: These geogrids are produced by weaving or knitting polymer fibers and then applying a protective coating to increase their resistance to environmental factors.
Applications: Commonly used in soil reinforcement and stabilization projects, particularly in aggressive environments.
Key Features:
Enhanced durability due to the protective coating.
Resistant to chemical exposure and UV degradation.
Suitable for long-term use in challenging environmental conditions.
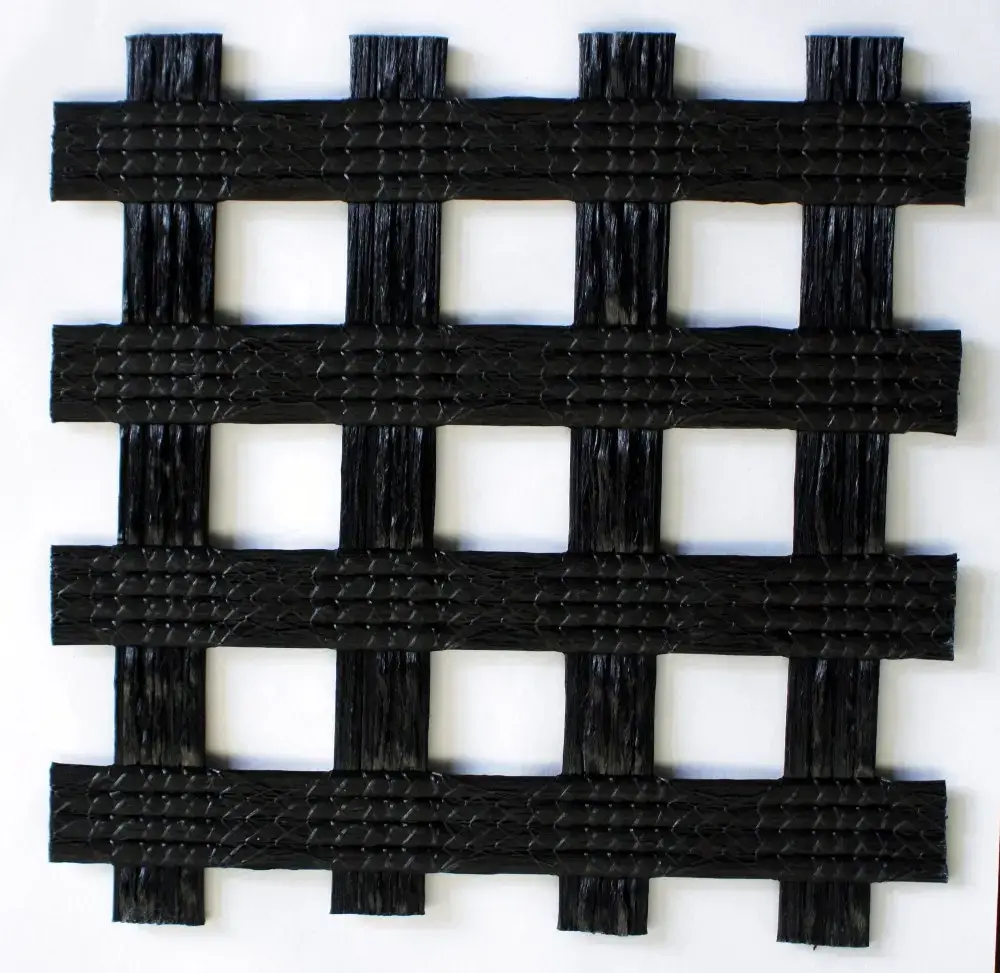
Size Specifications Table
| Specification | Details |
|---|---|
| Aperture Size | 30 mm - 80 mm |
| Width | 1 m - 6 m |
| Roll Length | 50 m - 200 m |
| Thickness | 1 mm - 3 mm |
| Material | Polyester, PVC coating |
Technical Specifications Table
| Specification | Details |
|---|---|
| Tensile Strength | 50 kN/m - 300 kN/m |
| Elongation | ≤10% |
| Durability | High chemical resistance |
| Application | Harsh environments, soil reinforcement |
Price Table
| Tensile Strength | Price (USD/m²) |
|---|---|
| 50 kN/m | $2.50 - $3.00 |
| 150 kN/m | $3.50 - $4.50 |
| 300 kN/m | $4.50 - $5.50 |
8. Fiberglass Geogrid
Description: Fiberglass geogrids are made from glass fibers, known for their high tensile strength and stiffness. They are used in asphalt overlays and pavement reinforcement.
Manufacturing: The glass fibers are coated with a polymer resin to improve adhesion with asphalt.
Applications: Primarily used in asphalt reinforcement to reduce cracking and increase the lifespan of roads and pavements.
Key Features:
High tensile strength and resistance to thermal degradation.
Reduces reflective cracking in pavements.
Cost-effective solution for asphalt reinforcement.
358789.webp)
Size Specifications Table
| Specification | Details |
|---|---|
| Aperture Size | 25 mm - 60 mm |
| Width | 1 m - 6 m |
| Roll Length | 50 m - 100 m |
| Thickness | 1 mm - 2.5 mm |
| Material | Fiberglass |
Technical Specifications Table
| Specification | Details |
|---|---|
| Tensile Strength | 30 kN/m - 200 kN/m |
| Elongation | ≤4% |
| Durability | High heat and UV resistance |
| Application | Asphalt reinforcement, roads |
Price Table
| Tensile Strength | Price (USD/m²) |
|---|---|
| 30 kN/m | $1.50 - $2.50 |
| 100 kN/m | $2.50 - $3.50 |
| 200 kN/m | $3.50 - $4.50 |
9. High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) Geogrid
Description: HDPE geogrids are made from high-density polyethylene, offering superior chemical and environmental resistance.
Manufacturing: Produced by stretching sheets of HDPE to create a grid structure.
Applications: These geogrids are commonly used in waste containment applications like landfill lining, as well as in areas exposed to aggressive chemical environments.
Key Features:
High resistance to chemical exposure and UV degradation.
Ideal for use in harsh environmental conditions, including landfills and containment systems.
Provides long-term soil stabilization.
 Geogrid971026.webp)
Size Specifications Table
| Specification | Details |
|---|---|
| Aperture Size | 30 mm - 80 mm |
| Width | 1 m - 6 m |
| Roll Length | 50 m - 100 m |
| Thickness | 1 mm - 3 mm |
| Material | HDPE |
Technical Specifications Table
| Specification | Details |
|---|---|
| Tensile Strength | 40 kN/m - 200 kN/m |
| Elongation | ≤12% |
| Durability | Excellent chemical resistance |
| Application | Chemical containment, landfill |
Price Table
| Tensile Strength | Price (USD/m²) |
|---|---|
| 40 kN/m | $2.00 - $3.00 |
| 100 kN/m | $3.00 - $4.00 |
| 200 kN/m | $4.00 - $5.00 |
10. Polypropylene (PP) Geogrid
Description: Polypropylene geogrids are manufactured from polypropylene, offering flexibility and resistance to environmental conditions like high moisture.
Manufacturing: Produced using extrusion and stretching techniques similar to HDPE geogrids.
Applications: Often used in roads, embankments, and areas with high moisture levels where stability and load distribution are needed.
Key Features:
Flexible and durable under wet conditions.
Good chemical resistance, especially in acidic soils.
Suitable for roads, subgrades, and embankments.
 Geogrid381978.webp)
Size Specifications Table
| Specification | Details |
|---|---|
| Aperture Size | 20 mm - 60 mm |
| Width | 1 m - 6 m |
| Roll Length | 50 m - 200 m |
| Thickness | 1 mm - 2.5 mm |
| Material | Polypropylene (PP) |
Technical Specifications Table
| Specification | Details |
|---|---|
| Tensile Strength | 40 kN/m - 150 kN/m |
| Elongation | ≤15% |
| Chemical Resistance | High resistance to acidic/alkaline soils |
| Application | Roads, subgrades, embankments |
Price Table
| Tensile Strength | Price (USD/m²) |
|---|---|
| 40 kN/m | $1.80 - $2.50 |
| 100 kN/m | $2.50 - $3.50 |
| 150 kN/m | $3.50 - $4.50 |
11. Steel-Plastic Composite Geogrid
Description: This is a composite geogrid that combines the high tensile strength of steel with the durability and flexibility of plastic (usually polypropylene or polyethylene).
Manufacturing: The steel bars are embedded into the plastic strips, and the composite is then stretched to create the grid.
Applications: Widely used in high-load areas like railways, highways, and heavy-load storage areas.
Key Features:
High tensile strength due to the steel core.
Excellent load-bearing capacity and durability.
Ideal for heavy-duty applications requiring additional strength.
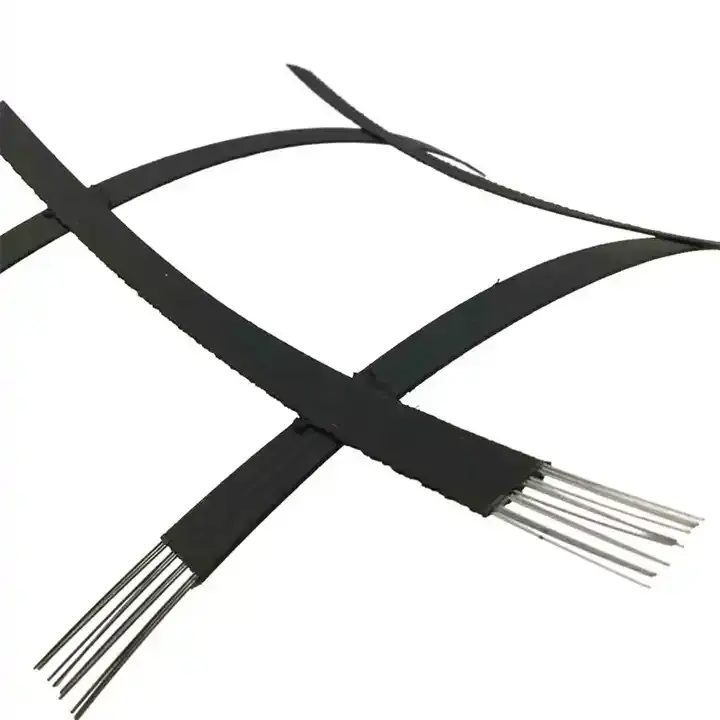

Size Specifications Table
| Specification | Details |
|---|---|
| Aperture Size | 25 mm - 80 mm |
| Width | 1 m - 6 m |
| Roll Length | 50 m - 200 m |
| Thickness | 2 mm - 5 mm |
| Material | Steel core + Plastic coating |
Technical Specifications Table
| Specification | Details |
|---|---|
| Tensile Strength | 60 kN/m - 500 kN/m |
| Elongation | ≤8% |
| Load-bearing Capacity | Extremely high |
| Application | Railways, highways, heavy loads |
Price Table
| Tensile Strength | Price (USD/m²) |
|---|---|
| 60 kN/m | $2.50 - $3.50 |
| 200 kN/m | $3.50 - $5.00 |
| 500 kN/m | $5.00 - $7.00 |
12. Geocomposite Geogrid
Description: Geocomposites combine geogrids with other materials such as geotextiles, geomembranes, or drainage layers to create multifunctional reinforcement solutions.
Manufacturing: These are made by bonding geogrids with other geosynthetic materials, depending on the required functionality.
Applications: Used in complex projects requiring both soil reinforcement and drainage, such as slope stabilization, erosion control, and road embankments.
Key Features:
Provides both reinforcement and filtration/drainage functions.
Reduces installation time and costs by integrating multiple functions.
Ideal for complex civil engineering projects like landfills and retaining walls.
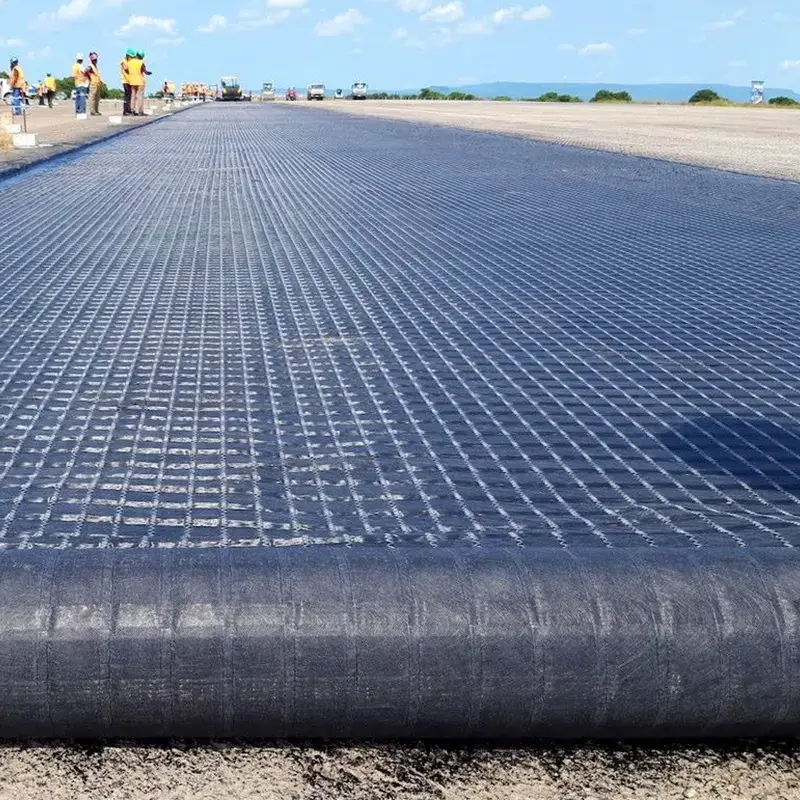

Size Specifications Table
| Specification | Details |
|---|---|
| Aperture Size | 30 mm - 80 mm |
| Width | 1 m - 6 m |
| Roll Length | 50 m - 100 m |
| Material | Geogrid + Geotextile/Geomembrane |
Technical Specifications Table
| Specification | Details |
|---|---|
| Tensile Strength | 40 kN/m - 300 kN/m |
| Elongation | ≤10% |
| Drainage Capacity | Integrated drainage properties |
| Application | Drainage and reinforcement, erosion control |
Price Table
| Tensile Strength | Price (USD/m²) |
|---|---|
| 40 kN/m | $2.50 - $3.50 |
| 150 kN/m | $3.50 - $4.50 |
| 300 kN/m | $4.50 - $6.00 |
13. Polyester (PET) Geogrid
Description: Made from high-strength polyester fibers, PET geogrids are widely used for soil reinforcement applications that require flexibility and durability.
Manufacturing: Polyester fibers are woven into grid patterns and coated for additional durability.
Applications: Ideal for soft soil stabilization, steep slopes, and retaining walls where flexibility is needed.
Key Features:
High tensile strength and flexibility.
Long-term resistance to environmental factors like temperature and moisture.
Frequently used in road construction, slope stabilization, and erosion control.
 Geogrid310249.webp)
Size Specifications Table
| Specification | Details |
|---|---|
| Aperture Size | 25 mm - 100 mm |
| Width | 1 m - 6 m |
| Roll Length | 50 m - 100 m |
| Thickness | 1 mm - 3 mm |
| Material | Polyester (PET) |
Technical Specifications Table
| Specification | Details |
|---|---|
| Tensile Strength | 50 kN/m - 300 kN/m |
| Elongation | ≤10% |
| UV Resistance | High |
| Application | Soil reinforcement, retaining walls, embankments |
Price Table
| Tensile Strength | Price (USD/m²) |
|---|---|
| 50 kN/m | $2.00 - $3.00 |
| 150 kN/m | $3.00 - $4.00 |
| 300 kN/m | $4.00 - $5.50 |
14. Bitumen-Coated Geogrid
Description: These geogrids are coated with bitumen, which enhances their adhesion to asphalt layers, making them ideal for use in road construction.
Manufacturing: After the geogrid is produced, it is coated with a layer of bitumen for improved bonding to asphalt.
Applications: Primarily used in road and pavement reinforcement, bitumen-coated geogrids prevent reflective cracking in asphalt overlays.
Key Features:
Excellent adhesion to asphalt, improving the lifespan of pavements.
Helps reduce the formation of cracks in roads.
Ideal for highway, airport, and road repairs.
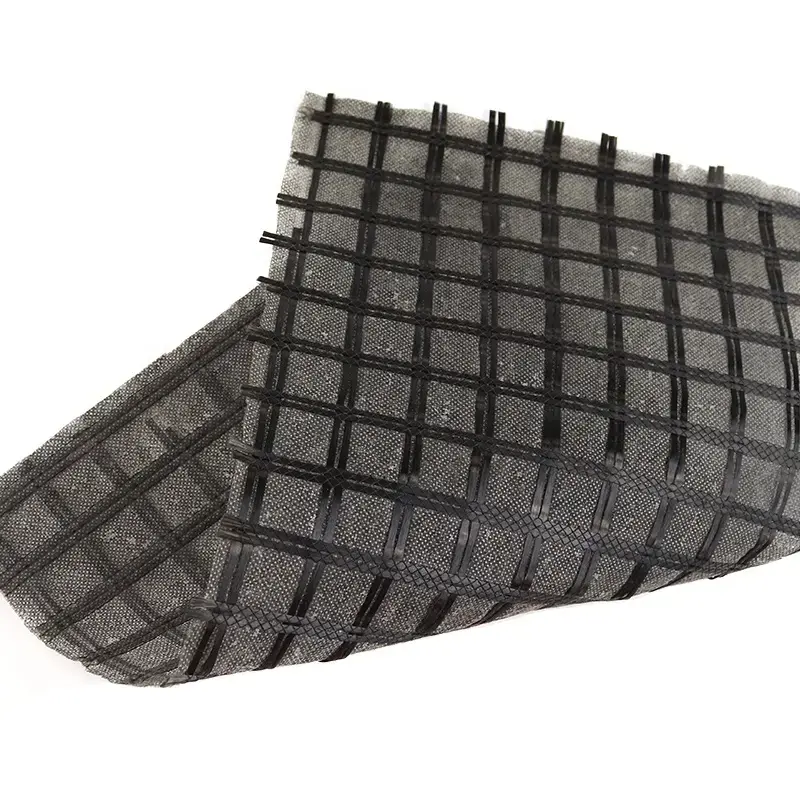

Size Specifications Table
| Specification | Details |
|---|---|
| Aperture Size | 25 mm - 75 mm |
| Width | 1 m - 6 m |
| Roll Length | 50 m - 100 m |
| Thickness | 1 mm - 3 mm |
| Material | Polyester/Fiberglass + Bitumen Coating |
Technical Specifications Table
| Specification | Details |
|---|---|
| Tensile Strength | 40 kN/m - 150 kN/m |
| Elongation | ≤5% |
| Bitumen Adhesion | Excellent for asphalt layers |
| Application | Asphalt reinforcement, roads, highways |
Price Table
| Tensile Strength | Price (USD/m²) |
|---|---|
| 40 kN/m | $2.00 - $2.50 |
| 100 kN/m | $2.50 - $3.50 |
| 150 kN/m | $3.50 - $4.50 |
15. PVC-Coated Geogrid
Description: PVC-coated geogrids are reinforced geogrids coated with a layer of polyvinyl chloride (PVC) for added durability and protection.
Manufacturing: The geogrid (typically polyester or polypropylene) is coated with PVC to improve its resistance to environmental factors.
Applications: Used in civil engineering projects like retaining walls, bridge abutments, and steep slopes, where additional protection from corrosion and abrasion is required.
Key Features:
Improved durability against moisture and chemical exposure.
Increased resistance to UV degradation and environmental damage.
Long-lasting performance in harsh environmental conditions.
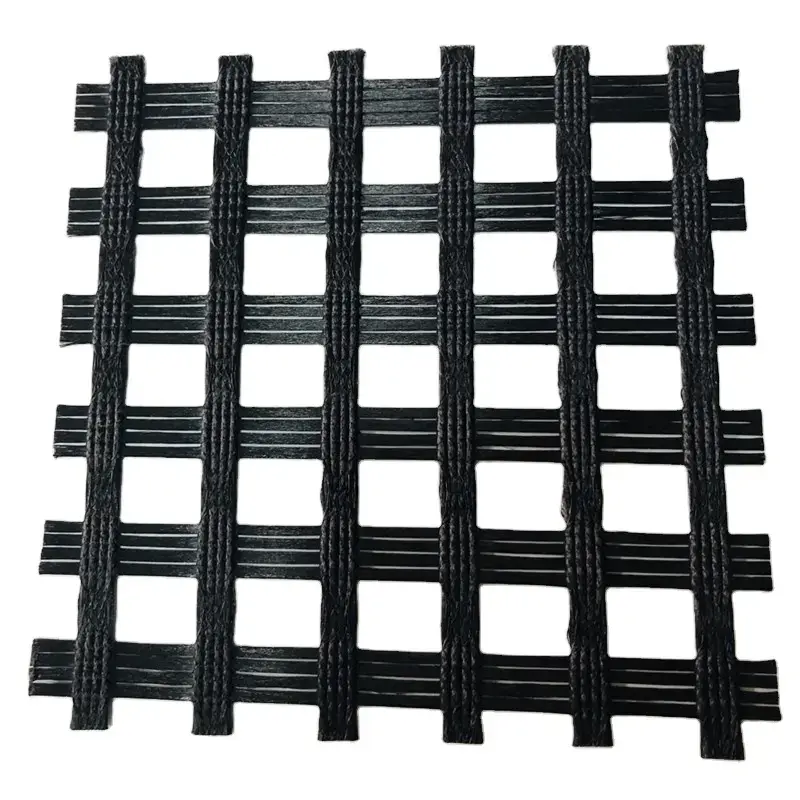
Size Specifications Table
| Specification | Details |
|---|---|
| Aperture Size | 30 mm - 80 mm |
| Width | 1 m - 6 m |
| Roll Length | 50 m - 100 m |
| Thickness | 1 mm - 3 mm |
| Material | Polyester/PP + PVC Coating |
Technical Specifications Table
| Specification | Details |
|---|---|
| Tensile Strength | 50 kN/m - 300 kN/m |
| Elongation | ≤10% |
| UV & Chemical Resistance | High |
| Application | Retaining walls, bridge abutments, slope stabilization |
Price Table
| Tensile Strength | Price (USD/m²) |
|---|---|
| 50 kN/m | $2.50 - $3.50 |
| 150 kN/m | $3.50 - $4.50 |
| 300 kN/m | $4.50 - $5.50 |
Summary of Geogrid Types and Applications
| Geogrid Type | Primary Direction | Material | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Uniaxial Geogrid | One direction | Polymer | Retaining walls, slope stabilization, embankments |
| Biaxial Geogrid | Two directions | Polymer | Road construction, base reinforcement, foundations |
| Triaxial Geogrid | Multi-directional | Polymer (Triangular) | Road foundations, general soil reinforcement |
| Extruded Geogrid | Multiple directions | Polymer | Road bases, landfills, embankments |
| Woven Geogrid | Two directions | Polyester | Retaining walls, embankments, heavy loads |
| Knitted Geogrid | Two directions | Polyester | Foundations, retaining walls, slope stabilization |
| Coated Geogrid | Variable | Polyester (coated) | Soil reinforcement in harsh environments |
| Fiberglass Geogrid | Multi-directional | Fiberglass | Asphalt reinforcement, pavement overlay |
Summary of Additional Geogrid Types and Applications
| Geogrid Type | Material | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| HDPE Geogrid | High-Density Polyethylene | Waste containment, landfills, chemical environments |
| Polypropylene (PP) Geogrid | Polypropylene | Roads, subgrades, embankments, wet areas |
| Steel-Plastic Composite Geogrid | Steel core, plastic coating | Railways, highways, heavy-load applications |
| Geocomposite Geogrid | Composite of geogrids, geotextiles | Complex projects, erosion control, drainage and reinforcement |
| Polyester (PET) Geogrid | Polyester | Road construction, soft soil stabilization, slopes |
| Bitumen-Coated Geogrid | Bitumen-coated polyester or fiberglass | Asphalt overlays, road and highway construction |
| PVC-Coated Geogrid | PVC-coated polyester or polypropylene | Retaining walls, bridge abutments, steep slopes |
These additional geogrids provide specialized solutions for more complex or demanding applications, such as chemical exposure, high-load reinforcement, and multi-functional needs like drainage and filtration. Selecting the right geogrid for a project requires consideration of soil conditions, environmental exposure, and the load-bearing requirements of the application.
749.webp)
897.webp)
942.webp)
237.webp)