Technical Properties and Composition of GCLs
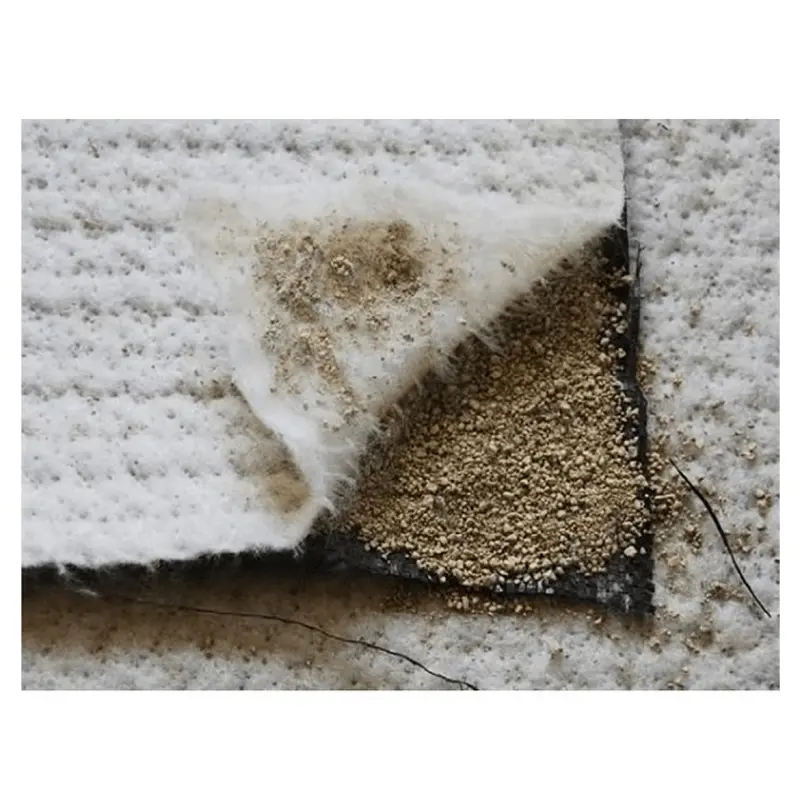
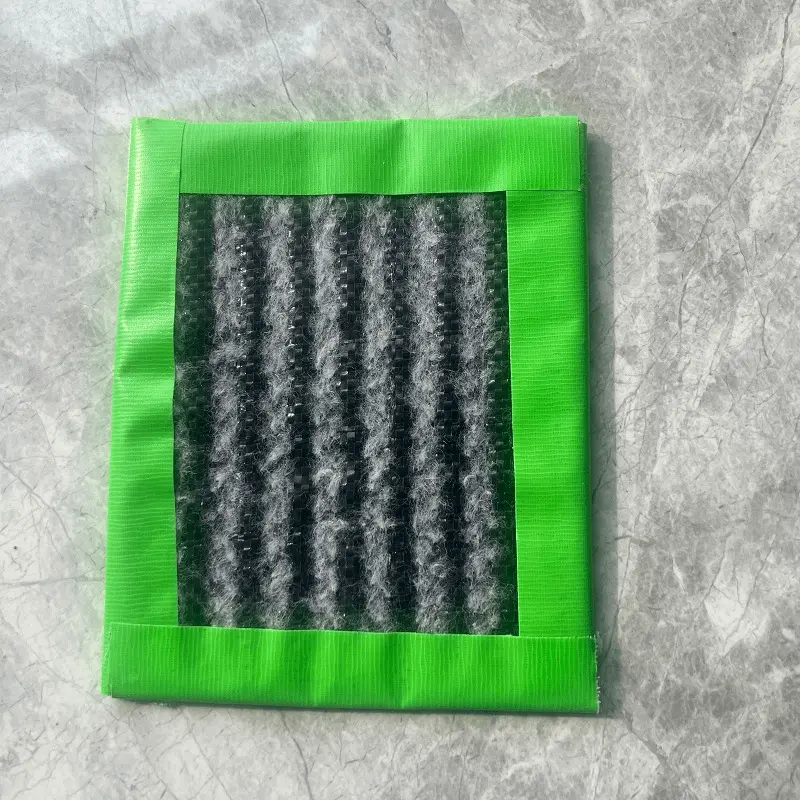
GCLs are composed primarily of sodium bentonite, a clay mineral known for its expansive characteristics and low permeability. Montmorillonite, the chief mineral in bentonite, swells significantly when hydrated, typically by 900% by volume or 700% by weight. This swelling property forms a low-permeability clay liner, offering equivalent hydraulic protection to several feet of compacted clay.
The structure of GCLs typically involves a layer of bentonite bonded between two geotextiles. These geotextiles provide structural support and encapsulate the bentonite, ensuring its effectiveness as a hydraulic barrier. In some cases, GCLs may also incorporate polymer additives to enhance their swelling capacity and mechanical properties.

Applications of GCLs in Kazakhstan
GCLs have found widespread application in Kazakhstan across various sectors, including landfills, dams, canals, and other containment structures. Their low hydraulic conductivity, durability, and ease of installation make them an ideal choice for these applications.
Landfills
GCLs are commonly used in landfill applications as caps and base liners. They provide an effective barrier against the leakage of contaminants from landfills, protecting the surrounding environment and groundwater. In Kazakhstan, with its growing waste management challenges, GCLs offer a sustainable and cost-effective solution for landfill lining systems.
Dams and Canals
Dams and canals require impermeable liners to prevent water leakage and maintain structural integrity. GCLs are frequently used in these applications due to their ability to withstand high pressures and provide a durable seal. Their resistance to freeze-thaw and wet-dry cycles further enhances their suitability for dam and canal lining.
Secondary Containment Structures
GCLs are also used in secondary containment structures, such as fuel storage facilities, to prevent the release of hazardous materials. Their low permeability and high shear strength make them ideal for these applications, ensuring the safety and environmental compliance of storage facilities.
Comparison with Compacted Clay Liners (CCLs)
GCLs offer several advantages over CCLs, making them a preferred choice for many geoenvironmental applications in Kazakhstan.
Thickness and Weight
GCLs have an average thickness of approximately 7mm, which is significantly less than CCLs. This results in reduced material usage and lower transportation and installation costs. Additionally, GCLs have a lower mass per unit area, further contributing to cost savings.
Material Thickness (mm) Mass per Unit Area (kg/m²) CCL Typically >300 High GCL 7 (Average) Lower than CCL Hydraulic Conductivity
GCLs exhibit lower hydraulic conductivity than CCLs, providing a more effective barrier against liquid and gas leakage. This is particularly important in applications where strict environmental regulations must be adhered to, such as landfills and fuel storage facilities.
Durability and Resistance
GCLs are more capable of withstanding freeze-thaw and wet-dry cycles than CCLs. This durability ensures long-term performance and reduces the need for maintenance and repairs.
Installation
GCLs are easier and faster to install than CCLs. They can be rolled out like a carpet, reducing labor costs and installation time. This efficiency is particularly beneficial in large-scale projects where quick installation is crucial.
Case Studies of GCL Applications in Kazakhstan
Several case studies in Kazakhstan demonstrate the effectiveness and benefits of GCLs in various applications.
Landfill Lining System
A landfill site in northern Kazakhstan used GCLs as the primary lining system. The GCLs were installed beneath a geomembrane to create a dual-composite liner system. The project team reported significant cost savings due to the reduced thickness and weight of the GCLs compared to CCLs. Additionally, the GCLs provided an effective barrier against leachate migration, ensuring compliance with environmental regulations.
Canal Lining Project
A canal lining project in southern Kazakhstan utilized GCLs to prevent water leakage and erosion. The GCLs were installed along the canal's bed and banks, providing a durable and impermeable lining system. The project team noted the ease of installation and the GCLs' ability to withstand high pressures and environmental conditions, such as extreme temperatures and soil movements.
Secondary Containment Structure
A fuel storage facility in western Kazakhstan incorporated GCLs in its secondary containment system. The GCLs were used to line the base and walls of the storage tanks, preventing the release of hazardous materials in the event of a leak. The facility's operator reported improved safety and environmental compliance, as well as reduced maintenance costs due to the GCLs' durability and resistance to chemicals.
Benefits and Future Prospects of GCLs in Kazakhstan
The benefits of GCLs in Kazakhstan are numerous and include cost savings, improved performance, and environmental compliance. Their ease of installation and durability further enhance their appeal for various geoenvironmental applications.
As Kazakhstan continues to develop its infrastructure and address environmental challenges, the demand for GCLs is expected to grow. The country's vast land area and diverse landscapes provide ample opportunities for the application of GCLs in landfills, dams, canals, and other containment structures.
Moreover, the ongoing research and development in GCL technology promise even better performance and cost-effectiveness in the future. Innovations in polymer additives, geotextile materials, and installation techniques will continue to drive the adoption and expansion of GCLs in Kazakhstan and beyond.
Conclusion
Geosynthetic Clay Liners (GCLs) have emerged as a vital technology in the field of geoenvironmental engineering, particularly in Kazakhstan. Their low permeability, durability, and ease of installation make them an ideal choice for various applications, including landfills, dams, canals, and secondary containment structures. GCLs offer significant advantages over traditional compacted clay liners (CCLs), including reduced thickness and weight, lower hydraulic conductivity, and improved resistance to environmental conditions. Case studies in Kazakhstan demonstrate the effectiveness and benefits of GCLs in real-world applications. As the country continues to develop its infrastructure and address environmental challenges, the demand for GCLs is expected to grow, driving further innovation and adoption of this technology.
![]() 1.5 Double-sided smooth HDPE geomembrane.pdf
1.5 Double-sided smooth HDPE geomembrane.pdf



897.webp)
942.webp)
237.webp)