Geotextiles are permeable fabrics that, when used in association with soil, have the ability to separate, filter, reinforce, protect, or drain. They are made from synthetic materials such as polypropylene, polyester, polyethylene, and other polymers.
Haoyang company mainly produces the filament needle-punched nonwoven geotextile, short staple fiber needle-punched nonwoven geotextile, plastic flat wire woven geotextile.
Four Aspects of Quality Control for Geotextiles in Haoyang
1. Quality Control of Raw and Auxiliary Materials:
To ensure the quality of finished products, we must ensure the quality of raw and auxiliary materials first. Following is the specific regulation of this aspect:
•To control and check the internal control standards for raw and auxiliary materials of filament geotextile enterprises;
•The raw and auxiliary materials shall be sampled according to the standard after arriving at the factory.
•The raw and auxiliary materials shall be sampled and retained after testing.
When the quality of the raw and auxiliary materials is up to the standard, Haoyang will accept the materials, otherwise they will return the materials.
2. Quality Control of Production Process:
To ensure the quality of the finished product, the quality control of the production process must be strengthened.
•Production order issuing process control.
•Recording of process parameters during production.
•Inspect and spot check the appearance of finished products during the production process.
•Measurement of the mass per unit area of the finished product during production.
•Geotextiles are packaged in a way that protects them from damage during transportation and storage. This includes using protective films and ensuring that rolls are properly secured.
•Proper storage conditions, such as keeping the geotextiles in a dry, cool environment, are essential to maintaining their quality and performance.
3. Quality Control of Finished Products:
The quality inspection of finished geotextiles involves many tests in terms of physical property test, mechanical property test, hydraulic performance test. We will introduce them in details later.
4. Traceability:
Traceability plays an important role in the process of product quality control.
Each batch of geotextiles is traceable back to its raw materials and production process. This allows for quick identification and resolution of any quality issues.
If there i s a quality problem of the sold product, it can be traced from the product information to the testing information of the finished product, the sample information of the finished product, the production process information of the finished product, the raw material information of the finished product, etc., so as to find the root cause of the quality problem and provide an important basis for the guarantee and improvement of product quality.
Test Standards of Finished Geotextiles
Haoyang strictly abides by the standards of geotextiles to test the finished products to ensure the quality. Geotextiles are subject to a variety of tests to ensure they meet the required performance criteria. Some of the key testing standards include:
NO. | Standard Code | Standard Name |
1 | GB/T 17639-2023 | Filament needle-punched nonwoven geotextile |
2 | GB/T 15788-2017 | Geotextiles and related products, wide strip tensile test method |
3 | ISO 10319:2008 | Geosynthetics- wide-width tensile test |
4 | ASTM D4595-11 | Standard test method for tensile properties of geotextiles by the wide-width strip method |
5 | ASTM D4632-06 | Method for determination of grab strength and tensile ratio of geotextiles |
6 | GB/T 13763-2010 | Geosynthetics - Determination of tear strength by trapezoidal method |
7 | ISO 13937-2-2000 | Textile. Tear properties of fabrics. Part 2:Determination of tear force of trouser-shaped test specimens (single tear method) |
8 | AST D4533/D4533M-15 | Standard test method of trapezoid tearing strength of geotextiles |
9 | GB/T 14800-2010 | Geosynthetics - static puncture test method CBR test |
10 | ISO 12236:2006 | Geosynthetics - static puncture test (CBR test) |
11 | ASTM D6241-14 | Standard test method for the static puncture strength of geotextiles and geotextile-related products using a 50mm probe |
12 | GB/T 15789-2005 | Geotextiles and geotextile-related products- Determination of water permeability characteristics normal to the place, without load |
13 | ISO 11058:2010 | Geotextiles and geotextile-related products- Determination of water permeability characteristics normal to the place, without load |
14 | ASTM D4491M-15 | Standard test method for water permeability of geotextiles by permittivity |
15 | GB/T 14799-2005 | Geotextiles and geotextile-related products-Determination of effective aperture - dry sieve method |
16 | ASTM D4751-12 | Standard test method for determining apparent opening size of a geotextile |
17 | GB/T 17634-1998 | Geotextiles and geotextile-related products-Determination of effective pore diameter - wet sieve method |
18 | ISO 12956:2010 | Geotextiles and geotextile-related products-Geotextiles and geotextile-related products- |
19 | GB/T 16422.2-1999 | Plastics methods of exposure to laboratory light source. Part 2: Xenon-arc lamps |
20 | ISO 4892-2:2013 | Plastics methods of exposure to laboratory light source. Part 2: Xenon-arc lamps |
21 | GB/T 16422.2-1997 | Plastics methods of exposure to laboratory light source. Part 3: UV lamps |
22 | ISO 4892-3:2013 | Plastics methods of exposure to laboratory light source. Part 3: UV lamps |
23 | GB/T 13761.1-2009 | Geosynthetics- Determination of thickness at specified pressures-Part 1:single layer |
24 | ISO 9863-1:2005 | Geosynthetics- Determination of thickness at specified pressures-Part 1:single layer |
25 | ASTM D5199-12 | Standard test method for measuring the nominal thickness of geosynthetics |
These standards are crucial for ensuring that geotextiles meet the required specifications for various applications. They provide a consistent and reliable framework for testing and evaluating the physical and mechanical properties of geotextiles, which is essential for their effective use in civil engineering projects.
Test Items of Finished Geotextiles
I: Physical Property Test
1. Thickness:
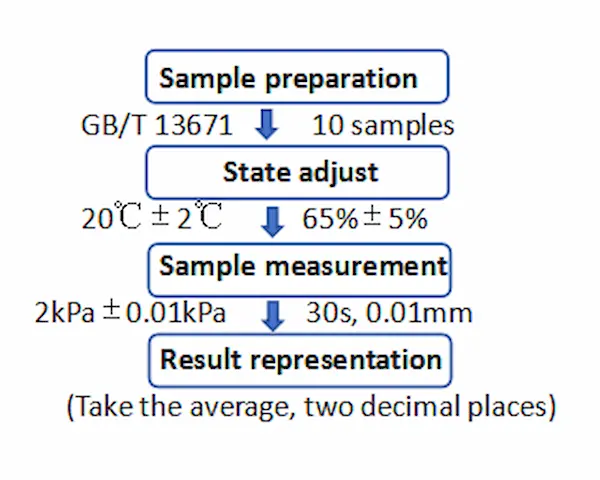
2. Mass Per Unit Area:
Method: A square or round specimen of known size (area 100 cm2) is cut from the entire width and length of the sample and weighed to calculate its mass per unit area.
It is a basic quality control measure and helps in ensuring consistency in the manufacturing process.
II:Mechanical property test
1. Tensile Strength:
Tensile strength tests are conducted to measure the maximum load the geotextile can withstand before breaking. This is crucial for applications requiring high strength and durability.
2. Grab Strength and Tensile Ratio:
The breaking force and elongation at break are obtained by applying increasing axial tension to the specimen until the specimen is perfectly formed. This test measures the tensile strength of the geotextile when it is subjected to a concentrated load. It is useful for evaluating the strength of the geotextile in localized areas.
355164.webp)
3. Tear Force of Trapezoidal Test :
Under specified conditions, the tearing force required to make the specimen tear from the initial notch and continue to expand is the trapezoidal tearing strength.
Elongation at break measures how much the geotextile can stretch before it breaks. This property is important for applications where flexibility is required.
4. CBR Test:
This test evaluates the ability of a geotextile to resist punctures from sharp objects. It is particularly important for geotextiles used in applications where they may be exposed to rocks or other sharp materials. It is used to assess the geotextile's resistance to puncture and its ability to maintain its integrity under load.
A square or circular sample of the geotextile is cut to the specified dimensions. The sample is placed over a support plate with a hole in the center. The hole is usually 80mm in diameter. The plunger is positioned directly above the center of the sample, ensuring that it is aligned with the hole in the support plate. The plunger is then lowered at a constant rate (usually 50 mm/min) until it punctures the geotextile. The maximum force required to puncture the geotextile is recorded. This force is known as the CBR puncture strength.The results are often expressed in terms of the puncture strength in kilonewtons (kN).
370620.webp)
III: Hydraulic Performance Test
1. Permittivity:
This test measures the water flow rate through the geotextile. It is crucial for determining the drainage and filtration capabilities of the geotextile.
2. Apparent Opening Size (AOS) Test :
The AOS test determines the size of the largest particle that can pass through the geotextile. This is important for assessing the geotextile's ability to retain fine particles while allowing water to pass through
Applications of Geotextiles
1. Road Construction:
•Foundation Reinforcement: Geotextiles can enhance the stability of road foundations, preventing soil erosion and settlement.
•Drainage: By providing good permeability, geotextiles help in draining water from the road base, reducing the impact of moisture on the foundation.
•Separation: Geotextiles can separate different types of soil or fill materials, preventing mixing and contamination.
2. Railway Construction:
•Track Bed Stability: Geotextiles can be used under railway track beds to improve stability, reducing maintenance costs.
•Drainage: Geotextiles effectively guide and drain water from beneath the track bed, preventing water accumulation and softening.
3. Water Management Projects:
•Dike and Dam Reinforcement: Geotextiles can be used to reinforce riverbanks, dikes, and reservoirs, preventing soil erosion and seepage.
•Filtration: In water management projects, geotextiles can act as a filtration layer, preventing fine particles from entering the drainage system while allowing water to pass through.
4. Environmental Protection:
•Landfill Liners: Geotextiles can be used as liners in landfills to prevent contaminants from leaching into groundwater.
•Ecosystem Restoration: Geotextiles can be used in vegetation restoration projects to stabilize soil and promote plant growth.
5. Building and Infrastructure:
•Foundation Reinforcement: Geotextiles can be used in the foundations of buildings and infrastructure to increase load-bearing capacity and stability.
•Waterproofing: Geotextiles can be combined with other waterproofing materials to form an effective barrier against water.
6. Coastal Protection:
•Breakwaters: Geotextiles can be used in the construction of breakwaters to protect coastlines from wave erosion.
•Beach Protection: Geotextiles can be used in beach protection projects to prevent sand loss.
7. Mine Reclamation:
•Tailings Management: Geotextiles can be used as liners and covers in tailings ponds to prevent tailings leakage and spread.
•Vegetation Restoration: In mine reclamation projects, geotextiles can help stabilize soil and promote vegetation recovery.
8. Sports Facilities:
•Artificial Turf: Geotextiles can be used as a base layer for artificial turf, providing good drainage and stability.
•Sports Fields: Geotextiles can be used in the sub-base of sports fields to improve surface flatness and durability.
9. Landscape Gardening:
•Slope Protection: Geotextiles can be used in landscape gardening for slope protection, preventing soil erosion.
•Planting Bags: Geotextiles can be made into planting bags for vertical and rooftop greening.
Geotextiles are widely used in various engineering projects due to their multifunctionality and adaptability.
Conclusion
Haoyang, with high quality raw materials, suitable production equipment, full-equipped laboratory and complete quality assurance system, is committed to providing guarantee for the realization of engineering design effect and contributing their own strength to the cause of environmental protection.
897.webp)
942.webp)
237.webp)