Geo textile, also known as geofabric, is a permeable polymer material used in geotechnical and civil engineering. Based on the manufacturing process, it can be classified into woven geotextile fabric and nonwoven geotextile fabric.
What is non woven geotextile fabric
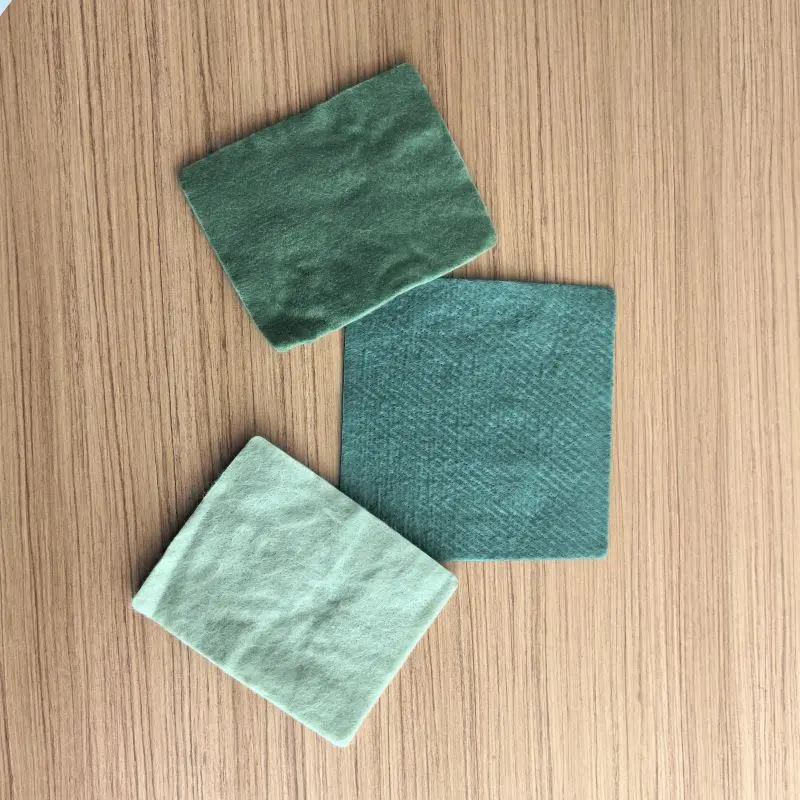

Non-Woven Geotextile fabric is a type of geosynthetic material produced through non woven processes, which do not involve traditional weaving or knitting. The distinctive feature of nonwoven geotextile is the absence of a discernible yarn structure and fabric hierarchy; instead, fibers are intertwined into a mesh-like structure through mechanical, heat fusion, or chemical bonding methods. These fibers can be either synthetic or natural. Common types of nonwoven geotextiles fabric include:
1, Spunbonded Geotextile: Geotextile prepared through the melt spinning process.
2,Needle-punched Short Fiber Geotextile: Geotextile made from short fibers using the needle-punching technique.
Nonwoven geofabric- Filament Spunbond nonwoven Needle-Punched Geotextile
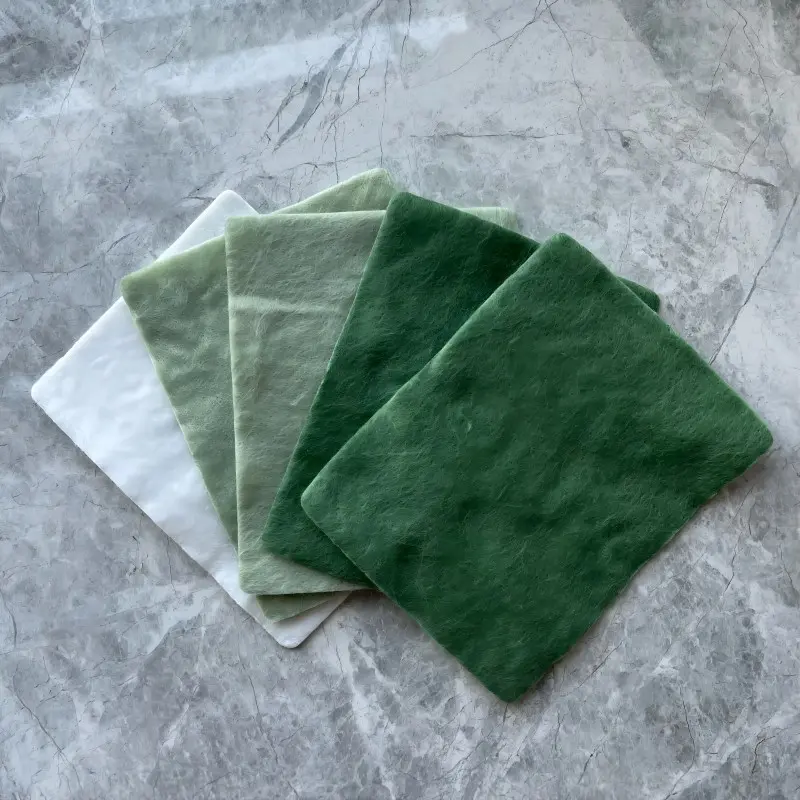

Long Fiber Spunbond Needle-Punched Geotextile, also known as long filament geotextile, has a distinctive production process. Its raw material is polyester chips (granular material), which are melted into filaments through equipment, woven into a net, and reinforced by needle-punching to create a nonwoven geotextile. In comparison to regular geotextiles, it features evident long filament threads and three-dimensional pores, often appearing in a pure white color. Under the same weight, its mechanical properties are higher than those of geotextiles made from other materials. For example, the tensile strength of a 400g/m² short fiber geotextile according to the new national standard is 15 kN, while a 400g/m² long filament geotextile can achieve over 20 kN.
Common specifications for long filament geotextiles are 200g/m², 400g/m², and 600g/m². The 200g/m² variant is typically used in projects requiring anti-filtration, while the 400g/m² and 600g/m² are often employed for reinforcement and protection (protecting geomembranes).
Processing of filament nonwoven Geotextile fabric
209076.webp)
The production process flow for long filament spunbond needle-punched geotextile are as follows:
1, Raw Material Preparation:
It includes slice filtering and transportation, here, we use 100% virgin raw material.
2, Melting and Extrusion:
Heat the granular material to a molten state.
Extrude the molten material to form continuous filaments.
3, Spinning:
The molten material is then metered and delivered in measured quantities through a metering pump. It enters the spinning assembly, where below the assembly is a spinneret plate. Upon exiting the spinneret plate, a molten fine stream is formed, which solidifies into primary fibers after cooling.
4, Web Formation:
Weave the spun filaments into a mesh-like structure to create a web.
5, Needle-Punching:
Reinforce the web through needle-punching, a mechanical process where barbed needles entangle the fibers, resulting in the formation of a nonwoven fabric.
6,Finishing:
Complete the production, resulting in the long filament spunbond needle-punched geotextile with distinctive features such as long filament threads, three-dimensional pores, and enhanced mechanical properties.
7,Cutting and Packaging:
Cut the geotextile into specified dimensions and package it for distribution, ready for use in various engineering applications.
Features of filament nonwoven Geotextile fabric
1, Excellent Mechanical Performance: It maintains outstanding strength and elongation even in challenging environments, ensuring the quality requirements of construction laying.
2, Strong Corrosion Resistance: It exhibits robust corrosion resistance, maintaining excellent durability in soils with varying pH levels, resulting in a longer lifespan. It is highly durable in both water and soil.
3, High Permeability with Unclogged Pores: The nonwoven structure formed by randomly oriented fibers provides flexibility and mobility, allowing it to maintain good permeability even under the compression of soil, and preventing pore blockage.
4, Easy Construction, Lightweight: It is easy to install and lightweight, providing convenient usability.
Applications
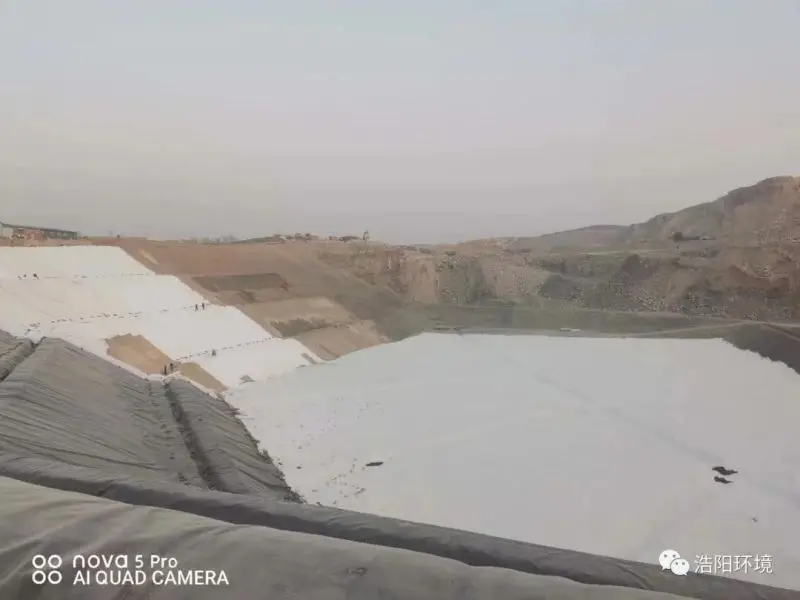

It can be widely used in landfills, saline-alkali marshes, and engineering projects such as highways, railways, dams, coastal beaches, etc., for anti-filtration, isolation, and drainage.
Specifications we can offer:
| Gram Weight | 100g/㎡-600g/㎡ |
| width | ≤6.6m |
| length | 50-100m or according to customer's requirements |
| color | white, green or customized |
Nonwoven geofabric- staple firber nonwoven Needle-Punched Geotextile

Short fiber nonwoven needle-punched geotextile is a type of geosynthetic material that is produced using a nonwoven manufacturing process. This geotextile is made from short synthetic fibers, typically polyester, with a fineness (fiber diameter) ranging from 6 to 12 deniers and a length between 54 to 64mm. The manufacturing process involves several steps, including opening, carding, web laying, and needle-punching.
Processing of staple fiber nonwoven geotextile fabric
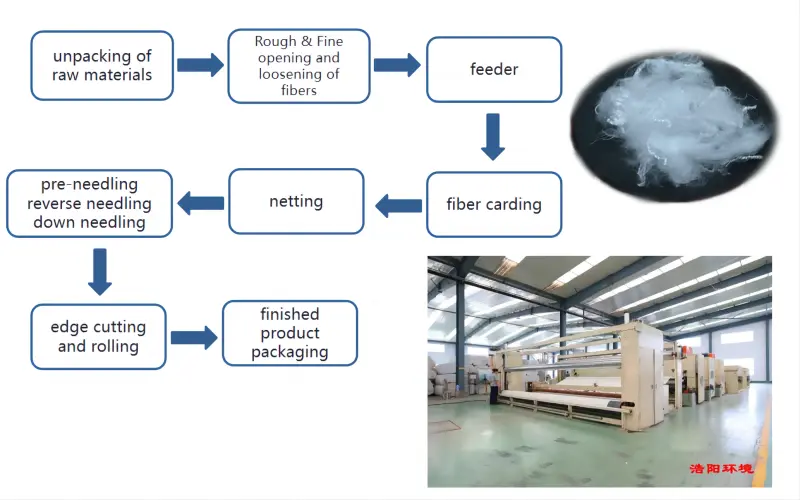
The processing of staple fiber nonwoven geotextile fabric involves several steps in the manufacturing process. Here's an overview of the typical process:
1, Raw Material Preparation:
The raw material for staple fiber nonwoven geotextile is usually synthetic fibers, such as polyester or polypropylene. The fibers are typically short in length and may be in the form of staple fibers.
2, Opening:
The raw fiber material goes through an opening process where it is loosened and separated to create a more uniform feedstock for subsequent processing.
3, Carding:
The opened fibers are carded, a process that aligns the fibers and removes impurities, resulting in a more uniform and parallel fiber arrangement.
4, Web Formation:
The carded fibers are laid out to form a web or mat. This web serves as the basis for the subsequent steps in the manufacturing process.
5, Pre-Needling:
Then the web may undergo a pre-needling process, which involves lightly needling the material to further consolidate and strengthen the web.
6, Needle-Punching:
The primary manufacturing step is needle-punching. Barbed needles are mechanically driven through the web, entangling the fibers and creating a cohesive nonwoven fabric. This process enhances the fabric's strength, durability, and overall performance.
7, Finishing, Rolling and Cutting:
The finished nonwoven geotextile fabric is often subjected to finishing treatments, such as calendaring or coating, to further enhance specific properties, such as water repellency or UV resistance. Then it is rolled onto large spools or rolls for easy transportation and storage. It may then be cut into specific dimensions according to project requirements.
Product performance
1, High Strength: The needle-punching process enhances the mechanical strength of the geotextile, ensuring it can withstand the stresses and loads encountered in geotechnical applications.
2, Filtration and Drainage: The open structure created by needle-punching allows for effective filtration and drainage of water, preventing soil erosion and maintaining stability.
3, Separation: The geotextile acts as a separator, preventing the mixing of different soil layers and ensuring the integrity of the engineering structure.
4, Durability: Short fibers, often made of polyester, contribute to the geotextile's durability and resistance to environmental factors, ensuring a longer service life.
5, Ease of Installation: The lightweight nature of the geotextile makes it easy to handle and install, contributing to the efficiency of construction projects.
6, Flexibility: The flexibility of the nonwoven structure allows the geotextile to conform to irregular surfaces and adapt to changes in the soil profile.
7, Corrosion Resistance: Short fiber nonwoven geotextiles, often made from synthetic materials like polyester, exhibit resistance to corrosion, making them suitable for various soil conditions.
Appliations
513340.webp)
Staple non woven geofabric finds versatile applications in geotechnical and civil engineering projects. Its high strength and flexibility make it suitable for soil stabilization, erosion control, and separation of soil layers. The fabric's efficient filtration and drainage capabilities contribute to effective use in drainage systems, road construction, and embankment protection. Its ease of installation, durability, and resistance to environmental factors further enhance its role in preventing soil erosion, promoting stability, and ensuring the longevity of various infrastructure projects.
specifications we can offer:
| Gram Weight | 100g/㎡-600g/㎡ |
| width | 2-6m |
| length | 50-100m or according to customer's requirements |
| color | white, green or customized |
Difference between filament needle punched geofabric and staple non woven geofabric
1, Different Appearance: In terms of appearance, the surface fibers of staple non woven geofabric are shorter, while the surface fibers of filament needle punched geofabric are longer.
2, Different Materials: Staple non woven geofabric is made from PET polyester short fibers, whereas filament needle punched geofabric is produced from polyester chips.
3, Price Difference: Usually,the price of staple non woven geofabric is lower than that of filament needle punched geofabric for the same specifications.
4, Application Scenarios: Filament needle punched geofabric, with superior performance, is generally suitable for reinforcement and anti-seepage in large-scale infrastructure projects such as water conservancy and highways with high standards. Staple non woven geofabric is used in smaller-scale projects related to waterproofing, anti-seepage, and isolation on land that is less industrialized.

897.webp)
942.webp)
237.webp)