1. Introduction to filament needle-punched non-woven geotextiles
Filament needle-punched non-woven geotextile is a geosynthetic material that is made by penetrating and stitching filament polymer fibers into each other through a needle-punching process. Commonly used materials for this kind of geotextile include polyester (PET), polypropylene (PP), etc. Filament needle-punched non-woven geotextiles are widely used in the engineering field due to their special manufacturing process and excellent performance. The latest implementation standard is GB/T 17639-2023.
2. Production of filament needle-punched non-woven geotextiles
Please refer to the following link for details
Filament non-woven waterproofing reinforced drainage geotextiles
3. Characteristics of filament needle-punched non-woven geotextiles
Polyester long fiber non-woven geotextile has excellent heat resistance and light resistance. Even after short-term exposure to temperatures close to 20°C, there is little change in performance. After a large number of tests and practices, it has been proven that polyester long fiber non-woven geotextiles have long-term corrosion resistance to various natural soils, moisture and microorganisms. Features include:
(1) High strength: The geotextile formed by the filament fiber needle punching process has excellent tensile strength and tensile breaking properties, and is suitable for engineering projects with high strength requirements. Under the same weight specifications, the tensile strength in all directions is higher than other needle-punched non-woven fabrics;
(2) Extremely high temperature resistance - resistant to high temperatures up to 230°C, and still maintains structural integrity and original physical properties under high temperatures;
(3) Good filtration performance: The acupuncture process of geotextile forms a uniform pore structure, which can provide good filtration and drainage functions and ensure soil stability and drainage performance.
(4) Corrosion resistance: Filament geotextiles are corrosion-resistant and can resist corrosion by chemicals, microorganisms in the soil and the natural environment.
(5) Ductility—Geotextiles have good elongation under certain stress, allowing them to adapt to uneven and irregular base surfaces;
(6) Multi-functional application: It is widely used in roads, railways, water conservancy projects, environmental protection projects and other fields as materials for isolation layers, filter layers, reinforcement layers, etc.
Filament needle-punched non-woven geotextiles can be customized according to needs during the project to meet the requirements of different engineering projects and provide good soil stability and engineering protection functions.
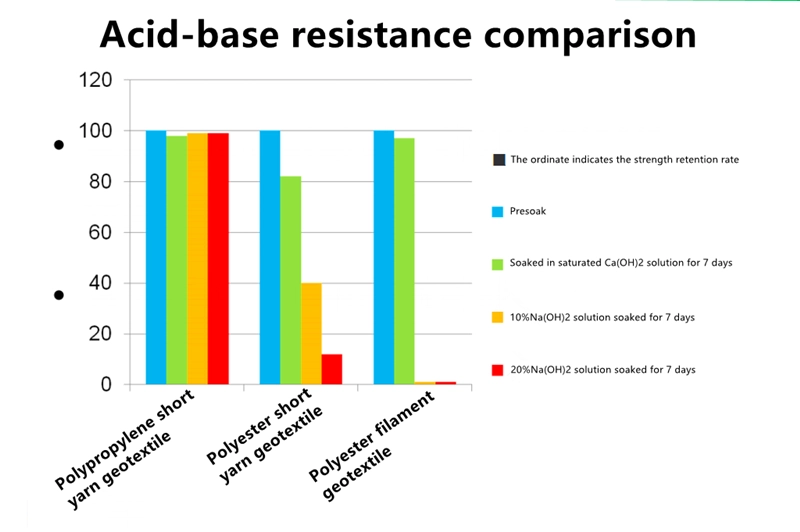
Comparison of acid and alkali resistance of filament geotextiles
4. The role of filament needle-punched non-woven geotextile
(1) Can play a permanent isolation role
It can isolate soil layers composed of different components and properties for a long time and prevent mixing; it has frost resistance and load-bearing requirements required for construction. That is, geotextiles are used to isolate building materials (such as soil and sand, sand and gravel, soil and concrete, etc.) with different physical properties (particle size, distribution, consistency and density, etc.). It prevents two or more materials from being lost or mixed, maintains the overall structure and function of the materials, and enhances the load bearing capacity of the structure.
(2) Has good filtering performance and anti-corrosion performance
Moisture can penetrate in all directions without pressure buildup. At the same time, it prevents soil loss and is beneficial to stability and anti-corrosion properties.
(3) Has reliable drainage performance
Due to the fluffy nature of its structure, it can effectively control the drainage of geotechnical engineering surfaces. Geotextile is a good water-conducting material. It can form drainage channels in the soil structure and remove excess liquid and gas inside the soil structure.
(4) Has good protective performance
Due to its good penetrability, extensibility and fluffiness, it can effectively protect the waterproof layer from potential mechanical damage.
(5) Has reinforcement properties
The bulkiness and high strength improve the overall stability of the project and increase its strength.
(6) Has closed performance
Geotextiles are combined with other materials (asphalt, plastic membrane) to form an impermeable barrier in the soil layer. (Mainly used for road repaving, repair, etc.).
5.Wide range of applications
(1) Used as reinforcement in retaining wall backfill, or used to anchor retaining wall panels. Build wrapped retaining walls or abutments.
(2) Reinforce flexible pavement, repair cracks on the road, and prevent reflective cracks on the road.
(3) Increase the stability of gravel slopes and reinforced soil to prevent soil erosion and freezing damage to the soil at low temperatures.
(4) The isolation layer between the road ballast and the roadbed, or the isolation layer between the roadbed and the soft foundation.
(5) The isolation layer between the artificial filling, rockfill or material field and the foundation, the isolation, filtering and reinforcement between different frozen soil layers.
(6) The filter layer on the initial upstream dam surface of the ash storage dam or tailings dam, and the filter layer of the drainage system in the backfill soil of the retaining wall.
(7) The filter layer around the underground drainage pipe or the gravel drainage ditch.
(8) The filter layer of water wells, pressure relief wells or baroclinic pipes in water conservancy projects.
(9) Geotextile isolation layer between roads, airports, railway ballast, artificial rockfill, etc. and the foundation.
(10) Vertical or horizontal drainage inside the earth dam, embedded in the soil to dissipate pore water pressure.
(11) Drainage behind the anti-seepage geomembrane or under the concrete face in earth dams or embankments.
(12) Eliminate water seepage around the tunnel and reduce external water pressure on the lining and water seepage around the buildings.
(13) Drainage of artificially filled sports ground foundation.
(14) Used to strengthen weak foundations in highways (including temporary roads), railways, embankments, earth-rock dams, airports, sports fields and other projects.
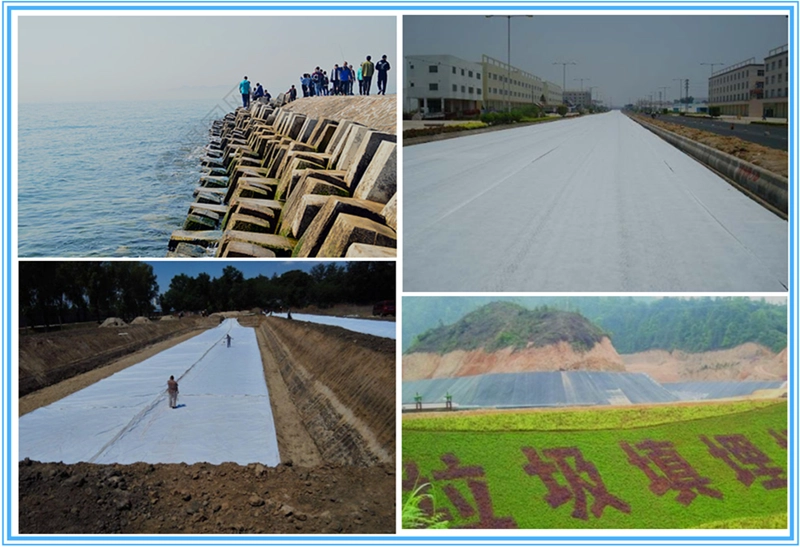

Specific application areas of filament geotextiles
6. Specific application areas
(1) Water conservancy projects: sea dikes, river dikes, and lake dikes up to standard; reservoir reinforcement projects; reclamation projects; flood control and rescue.
Highway, railway and airport projects: soft foundation reinforcement; slope protection; road surface anti-reflective crack structural layer; drainage system; green isolation belt.
(2) Electrical engineering: nuclear power plant foundation engineering; thermal power ash dam engineering; hydropower station engineering.
7. Laying process of polyester filament geotextile:
(1) Storage, transportation and handling of geotextiles
Geotextile rolls should be protected from damage before installation and unfolding. Geotextile rolls should be stacked in a flat place that does not accumulate water. The stack height should not exceed the height of four rolls, and the identification piece of the roll can be seen. Geotextile rolls must be covered with opaque material to protect against UV aging. During the storage process, the integrity of the label and the integrity of the data must be maintained.
During transportation (including on-site transportation from the material storage location to the work site), geotextile rolls must be protected from damage.
Physically damaged geotextile rolls must be repaired. Geotextiles that are severely worn cannot be used. Any geotextile that comes into contact with leaked chemical reagents is not allowed to be used in this project.
(2) How to lay geotextile:
A. Use manual rolling; the cloth surface should be smooth, with appropriate allowance for deformation.
B. The installation of filament or short-filament geotextiles usually uses several methods such as overlapping, sewing and welding. The width of stitching and welding is generally more than 0.1m, and the width of overlap is generally more than 0.2m. Geotextiles that may be exposed for a long time should be welded or stitched.
(3) Sewing of geotextile
A. All stitching must be done continuously (for example, spot stitching is not allowed). Geotextiles must overlap by a minimum of 150mm before overlapping. The minimum stitch distance from the selvedge (the exposed edge of the material) is at least 25mm.
B. The sewn geotextile seams include 1 row of chain-lock stitching. The thread used for suturing should be a resin material with a minimum tension of more than 60N, and have chemical corrosion and ultraviolet resistance that is equivalent to or exceeds that of geotextiles.
C. Any "missing stitches" on the sewn geotextile must be re-sewn at the affected location.
D. Corresponding measures must be taken to prevent soil, particulate matter or foreign matter from entering the geotextile layer after installation.
E. The overlap of cloth can be divided into natural overlap, seam or welding according to the terrain and use function.
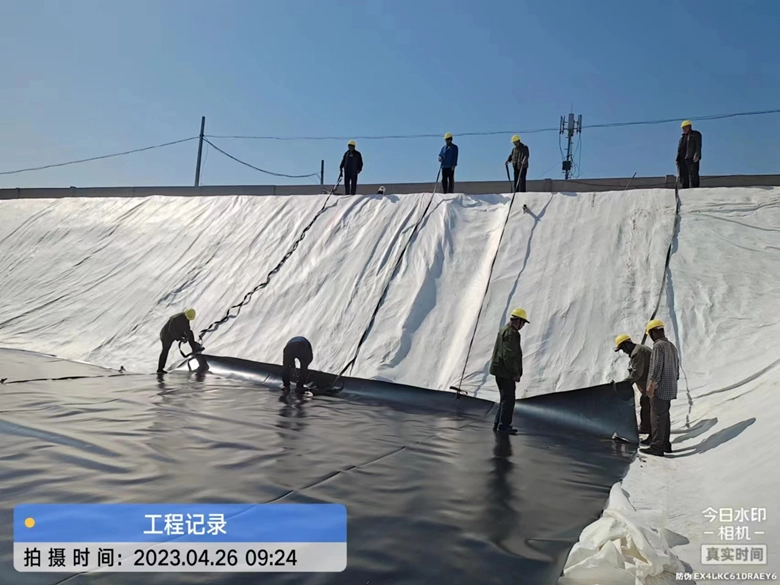

Filament geotextile laying site
8. The filaments do not hinder the later maintenance of the geotextile
Filament non-woven geotextiles usually require certain maintenance during use to ensure their performance and functionality:
(1) Cleaning and maintenance: Regularly clean debris, sediment, etc. on the surface of the geotextile to maintain permeability and maintain its good filtration and drainage functions.
(2) Check for damage: Regularly check whether the surface of the geotextile is damaged, torn or deformed, especially after construction and after extreme weather (such as strong winds, heavy rain). Repair or replace problems promptly if problems are discovered.
(3) Prevent damage from sharp objects: Avoid sharp objects or sharp objects from directly contacting the surface of the geotextile to avoid scratching or damaging its fiber structure.
(4) Avoid pollution: Long-term contact with chemical substances such as oil, acid, alkali, etc. may cause damage to the geotextile, so pollution must be avoided.
(5) Reasonable use: During the construction process, follow the correct installation and use methods to ensure that the geotextile can achieve its best effect.
Regular maintenance and inspection help extend the service life of the filament non-woven geotextile and maintain its performance and functionality, thereby ensuring the stability and durability of the project.
For other products of our company, please refer to the following link.
White waterproof filament non-woven geotextile for tunnel
Drainage system special black plastic flat wire woven film yarn geotextile
1.5mm smooth impermeable HDPE geomembrane in India
leachate collection system landfill liner material geosythetic clay liner waterproof blanke
White road bridge special 3D composite drainage net selling in the United States
![]() 200g Staple fiber non-woven geotextile.pdf
200g Staple fiber non-woven geotextile.pdf
![]() 300g PET geotextiles test report.pdf
300g PET geotextiles test report.pdf




503.webp)
759.webp)

861.webp)
